A company has a long term loan from a bank at a fixed rate of interest. It expects interest rates to go down. Which of the following instruments can the company use to convert its fixed rate liability to a floating rate liability?
A trader comes in to work and finds the following prices in relation to a stock: $100 spot, $10 for a call expiring in one year with a strike price of $100, and $10 for a put with the same expiry and strike. Interest rates are at 5% per year, and the stock does not pay any dividends. What should the trader do?
Security A and B both have expected returns of 10%, but the standard deviation of Security A is 10% while that of security B is 20%. Borrowings are not permitted. A portfolio manager who wishes to maximize his probability of earning a 25% return during the year should invest in:
The theta of a delta neutral options position is large and positive. What can we say about the gamma of the position?
A pension fund has $100m in liabilities due in the future with an average modified duration of 20 years. The fund also holds a fixed income portfolio worth $125m with an average duration of 15 years. Which of the following approaches would be best suited for the pension fund to cover its interest rate risk?
A US treasury bill with 90 days to maturity and a face value of $100 is priced at $98. What is the annual bond-equivalent yield on this treasury bill?
A portfolio comprising a long call and a short put option has the same payoff as:
A bank advertises its certificates of deposits as yielding a 5.2% annual effective rate. What is the equivalent continuously compounded rate of return?
Consider a portfolio with a large number of uncorrelated assets, each carrying an equal weight in the portfolio. Which of the following statements accurately describes the volatility of the portfolio?
According to the CAPM, the expected return from a risky asset is a function of:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Rebalancing frequency is a consideration for a risk manager when assessing the adequacy of delta hedging procedures on an options portfolio
II. Stock options granted to employees that are exercisable 5 years in the future will lead to a decline in the share price 5 years hence only if the options are exercised.
III. In a delta neutral portfolio, theta is often used as a proxy for gamma by traders.
IV. Vega is highest when the option price is close to the strike price
A large utility wishes to issue a fixed rate bond to finance its plant and equipment purchases. However, it finds it difficult to find investors to do so. But there is investor interest in a floating rate note of the same maturity. Because its revenues and net income tend to vary only predictably year to year, the utility desires a fixed rate liability. Which of the following will allow the utility to achieve its objectives?
An investor has a bullish outlook on the market. Which of the following option strategies would suit him?
I. Risk reversal
II. Collar
III. Bull spread
IV. Butterfly spread
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
What is the current conversion premium for a convertible bond where $100 in market value of the bond is convertible into two shares and the current share price is $50?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Caps allow the buyer of the cap protection against rise in interest expense
II. Floors offer investors protection from downward movement in interest rates
III. Collars can be used as hedges
IV. Both caps and collars can be used to hedge against widening credit spreads
The objective function satisfying the mean-variance criterion for a gamble with an expected payoff of x, variance var(x) and coefficient of risk tolerance is λ is:
A)
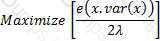
B)
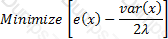
C)
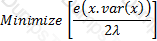
D)
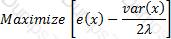
A 15 year bond is trading at par. Its modified duration is 11 years and convexity is 80. Determine the price of the bond following a 10 basis point increase in interest rates
If the implied volatility is known for a call option, what can be said about the implied volatility for a put option with the same strike and maturity?
When hedging an equity portfolio with index futures that carry no basis risk, the number of futures contracts to hold is determined by:
Which of the following statements is not correct with respect to a European call option:
Continuously compounded returns for an asset that increases in price from S1 to S2 over time period t (assuming no dividends or other distributions) are given by:
Which of the following statements is true:
I. The maximum value of the delta of a call option can be infinity
II. The value of theta for a deep out of the money call approaches zero
III. The vega for a put option is negative
IV. For a at the money cash-or-nothing digital option, gamma approaches zero
The underlying objective in decisions relating to capital structure is to:
If interest rates and spot prices stay the same, an increase in the value of a call option will be accompanied by:
A risk analyst working for an asset manager with a large debt portfolio is tasked with determining the suitability of using a traded debt ETF as a hedge against the value of the debt portfolio. He/she calculates the minimum variance hedge ratio to be exactly 1.0.
Given the above facts, which of the following statements are certainly true:
I. The ETF represents a perfect hedge for the portfolio
II. The volatility of the portfolio is the same as that for the ETF
III. The ETF cannot be used as an effective hedge for the debt portfolio
IV. None of the above
A stock is selling at $90. An investor writes a covered call on the stock with an exercise price of $100 in return for a premium of $3 per share. What would be the maximum gain or loss per share that the investor could make on this position?
An asset manager is of the view that interest rates are currently high and can only decline over the coming 5 years. He has a choice of investing in the following four instruments, each of which matures in 5 years. Given his perspective, what would be the most suitable investment for the asset manager? Assume a flat yield curve.
Which of the following markets are characterized by the presence of a market maker always making two-way prices?
Which of the following statements is not true about covered calls on stocks