Which parameter is expected to increase in the presence of cardiac tamponade?
What minimum number of poorly-visualized contiguous left ventricular (i_V) regional wall segments indicate the use of contrast agents for LV endocardial border definition?
Mid to distal septal akinesis in post-stress imaging of the apical four-chamber view is suggestive of disease in which coronary artery?
Which of the following conditions will increase in seventy with Valsalva maneuver?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does the left ventricular filling pressure equalize with left atrial pressure?
Which region of the aorta is being measured to assess the critical finding in this image?
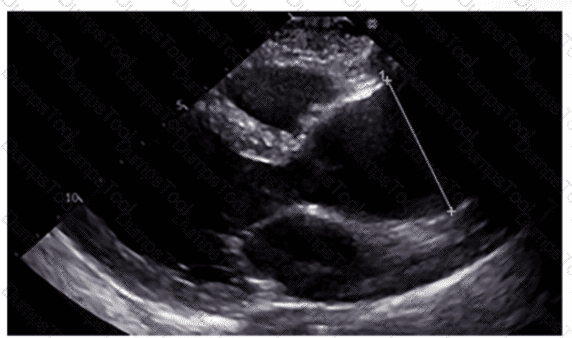
Which type of mass is typically attached to the fossa ovalis of the left atrium?
Which statement is considered true regarding tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE)?
Which of the following can be calculated from the peak tricuspid regurgitant velocity?
Which finding does peak mitral valve regurgitant Doppler velocity reflect?
Which left ventricular regional wall segment is indicated by the arrow on this image?
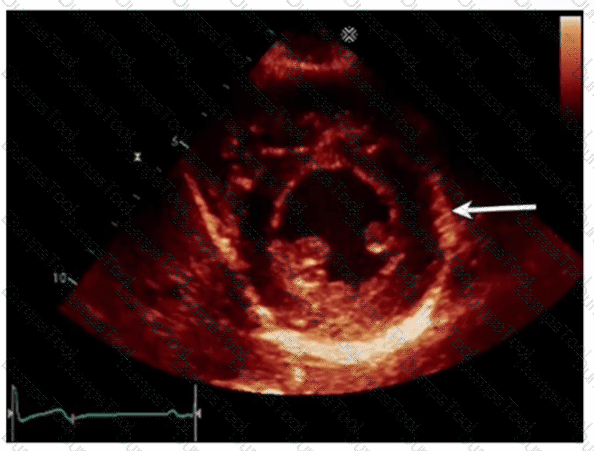
What is the incidental finding seen by color Doppler in this four-chamber view of a patient with left atrial enlargement?
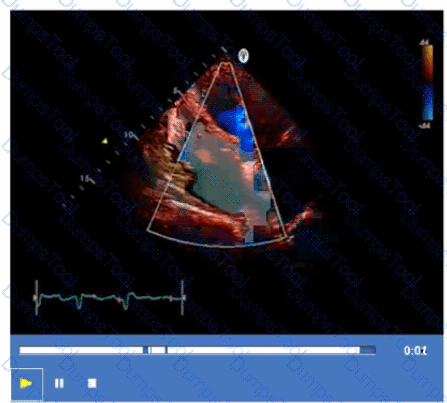
In cardiac tamponade, how do transvalvular pressure gradients change during expiration?
A patient presents with tender, red lesions on their fingers and toes (Osier nodes). Which finding is most likely?
Which method of measuring left atrial size is most recommended and most accurate?
Which condition is most plausible based on the finding indicated by the arrow on this image?
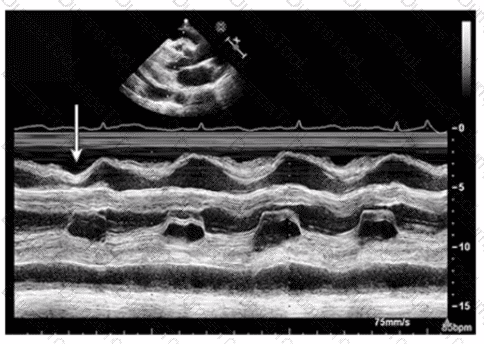
Which view best demonstrates a wall thickening abnormality of the apical lateral segment?
The 'P' wave of an electrocardiogram relates to which echocardiography event?
Which view is best for assessing atrial situs in the presence of congenital heart disease?