Per the example:
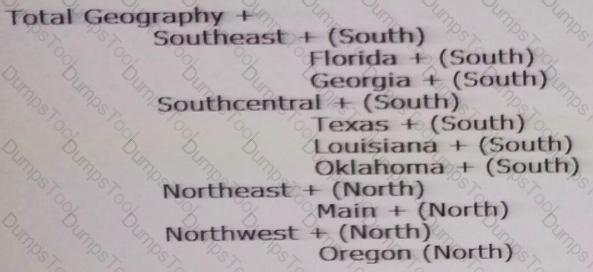
You have a property definition called Region with possible valid values "east", "West", "North", and "South".
How do you set this property for end users?
Identify two reasons to build validations using derived properties vs. validations using property queries?