Maternal fever can cause fetal tachycardia because the increased maternal temperature:
A fetus displays a baseline heart rate of 125 beats per minute with moderate variability. During a contraction, the baseline rate drops abruptly to 80 beats per minute with gradual return to baseline over 90 seconds. This is classified as:
To differentiate a fetal dysrhythmia from artifact, it is important to recognize that artifact appears as deflections that are:
A fetal heart rate pattern shows no accelerations or decelerations. It would be interpreted as a Category II pattern if it occurred with:
When fetal arterial blood pressure increases, the baroreceptors send impulses to the vagus nerve resulting in:
The ratio of oxyhemoglobin to the total amount of hemoglobin available is called oxygen
(Full question statement)
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends continuous electronic fetal monitoring in pregnancies when there is:
A nonstress test is nonreactive in a 36-week gestational age fetus. Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is applied with no fetal response. The next step is to proceed to:
An electronic fetal monitoring factor that best correlates with fetal well-being is:
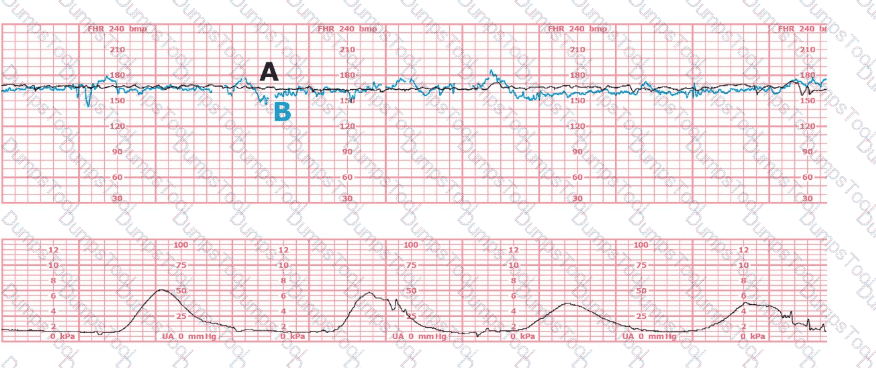
The black pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby A. The blue pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby B. A possible etiology of the baseline fetal heart rate of Baby A is:
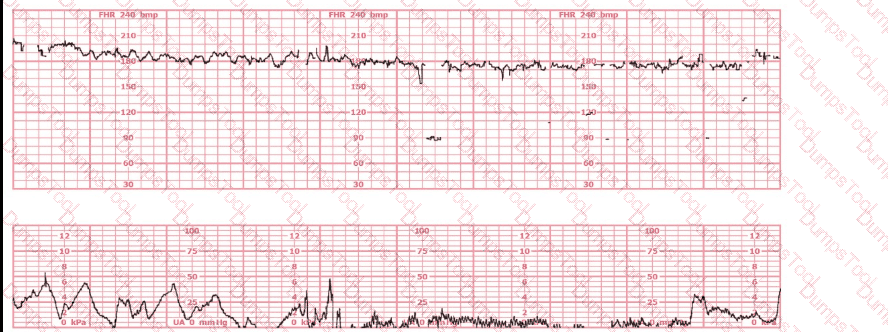
A 30-year-old woman (G2P0) is experiencing preterm labor at 26-weeks gestation. She is receiving magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Her external fetal monitoring tracing over the past 30 minutes is shown. The next step would be to:
Maternal conditions of autoimmunity can result in fetal heart block due to antibodies that target:
A pattern of recurrent variable decelerations would move from Category II to Category III if what fetal heart rate change occurs?
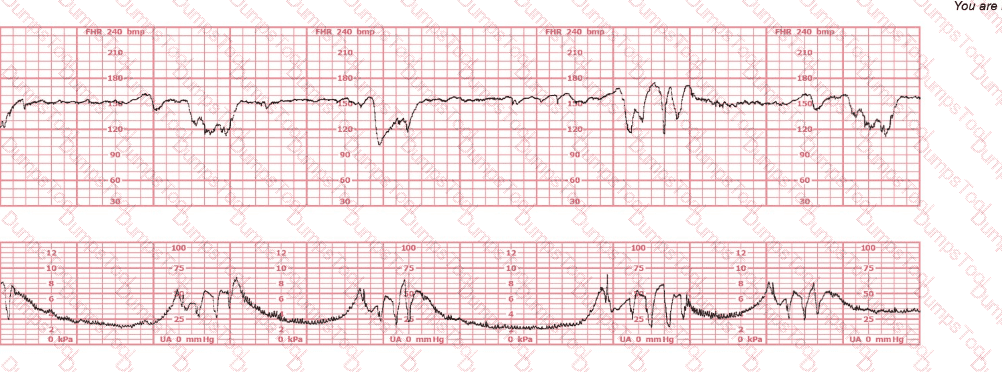
A woman at 39-weeks gestation is being induced. She has chronic hypertension controlled by methyldopa (Aldomet). Spontaneous rupture of membranes has occurred; she is 10 cm dilated and at +1 station. The fetal monitor tracing shown is obtained by spiral electrode and tocodynamometer. The next best appropriate action is to:
A fetal heart rate tracing is abnormal. A change in maternal position and oxygen administration do not correct the pattern. Following birth, a fetal cord blood sample is taken:
pH = 7.25
PaCO₂ = 46 mm Hg
PaO₂ = 20 mm Hg
HCO₃ = 22 mEq/L
Base deficit = –4 mEq/L
These results are best interpreted as:
The baseline heart rate of a 28-week fetus is 170 bpm. The next step is to:
(Full question statement)
The fetal heart rate tracing shown is obtained upon the woman's admission to labor and delivery. This tracing is most consistent with what maternal condition?

Usually, the duration of an early deceleration in comparison with the contraction is:
A 30-minute tracing with moderate variability, accelerations, and one variable deceleration would be classified as:
(Full question statement)
A woman at 39-weeks gestation is in labor, progressing normally. The baseline fetal heart rate has increased from 125 to 150 beats per minute over the last hour with moderate variability. What is the next step?
During the second stage of labor, a period of bradycardia develops. The fetal heart rate baseline variability is moderate. The most likely cause of this bradycardia is:
When documenting the occurrence of late decelerations in the medical record, what should be charted?
A nulliparous woman at term presents with leaking fluid. Rupture of membranes confirmed. After 6 hours she is completely dilated, +2 station, has been pushing 2 hours with oxytocin at 10 mU/min. The fetal tracing is shown. What is the next step in management?
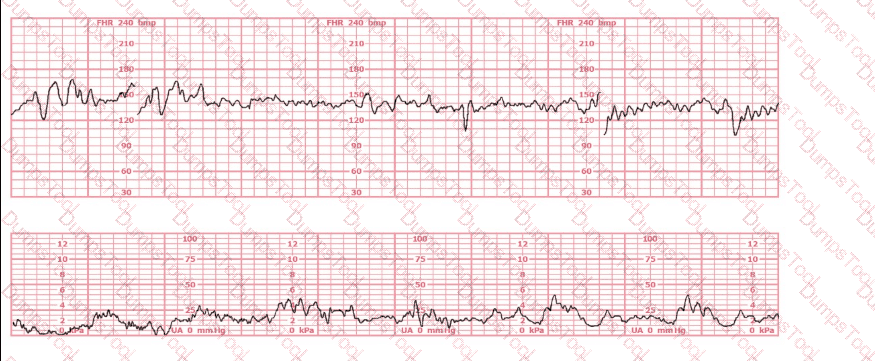
This fetal heart rate tracing is from a woman in the second stage of labor. This tracing is best interpreted as:
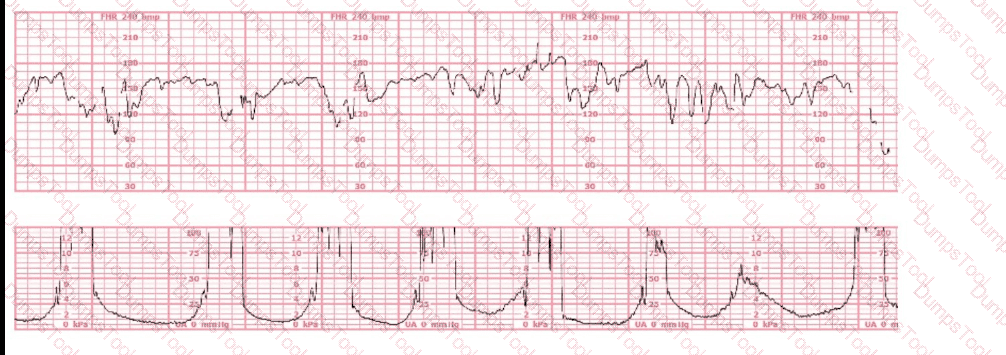
When a difference in interpretation occurs over a non-emergent electronic fetal heart rate tracing, the first step toward resolution is to: