A 78-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with chest pain. His electrocardiogram and blood work confirm an acute myocardial infarction. He is admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Three days later, he develops right-sided abdominal pain. An ultrasonogram reveals an inflamed gallbladder with no evidence of stones. He does not improve after 48 hours of antibiotics. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 39-year-old woman comes to the office for a periodic health examination. She reports that her father had a recent diagnosis of breast cancer (at age 62 years) and that a paternal aunt had ovarian cancer in her early 40s. The results of mammography are normal. Which one of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for this patient?
A 59-year-old woman is referred to you because of a 2-month history of left nipple discharge. She is otherwise healthy and is not on any medication. There are no palpable lesions on breast examination. She is able to express a small amount of blood-tinged liquid from her breast. Which one of the following would be the best next step?
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, aborta 0, has just delivered a full-term newborn via spontaneous vaginal delivery after 4 hours of labor. Following oxytocin administration and placental expulsion, there continues to be a steady trickle of bright red blood from her vagina. On examination, the placenta is intact and the fundus feels firm. Her vital signs are within normal range.
Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
An 84-year-old woman is brought by ambulance to the emergency department after she was found by a neighbour. She had fallen, sustained a hip fracture, and was unable to move for the past 2 days. After starting rehydration, she reports hip pain and numbness and tingling in both her legs. Physical examination reveals faint pulses in both legs and severely swollen lower legs that are painful to palpation. The urine in the Foley catheter bag seems to be darker than normal. Which one of the following is the best next step?
An 18-year-old woman comes to the office because of fatigue. She tells you she is struggling in her first year of university. She mentions that she spends much of her time rewriting her notes and filing and organizing her study materials. She is doing all the work in her group assignments because she feels others cannot do the work to a high enough standard. She has abandoned all enjoyable activities and seems to be constantly working and worrying about her grades. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, presents for her 1st antenatal visit. She states she is at 26 weeks' gestation and is healthy. On abdominal examination, her fundus is palpated at the umbilicus. Which one of the following is the most likely explanation for this finding?
A 38-year-old man is brought by his wife to the Emergency Department with fatigue, dizziness, and nausea after completing a hiking tour on a hot, humid day. His wife became worried after he had collapsed. He has been sweating heavily and vomited twice on the drive in. His medical history is unremarkable, and he takes no medications. His vital signs on arrival are as follows:
Blood pressure
85/57 mm Hg
Heart rate
120/min
Respiratory rate
18/min
Temperature
40.1 °C
Oxygen saturation
95%, room air
—
On physical examination, the patient's skin is dry, flushed, and warm to the touch. He has a diffuse erythematous papular rash. Findings of a thorough physical examination are otherwise unremarkable. An electrocardiogram shows sinus tachycardia. Which one of the following is the best next step?
You are covering for your colleague who is on vacation this week. You receive the results from an ultrasonography that had been ordered for a 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, aborta 0. The ultrasonography-estimated fetal weight is below the fifth percentile for 30 weeks' gestation; gestational age was confirmed by an earlier ultrasonogram. The amniotic fluid volume is within normal range. Her first child's birth weight was 2800 g at full term. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 1, aborta 0, gave birth to a newborn who is hypotonic with a large protruding tongue and brachycephaly. The newborn has a single palmar crease bilaterally and short, broad hands with a curved fifth digit. These features best support a clinical diagnosis of which one of the following?
A 22-year-old woman presents to the office for episodic mood changes that her boyfriend has noticed. During such episodes, she cries suddenly, is irritable and sad, and withdraws from socializing. Which one of the following would be most useful in establishing a diagnosis?
A 32-year-old woman presents to the office with questions related to the mRNA vaccines that are approved for COVID-19. She is a health care worker. She gave birth to a healthy child 2 months ago. Before being immunized, which one of the following is the most important detail to elicit from the patient's history?
A mother brings her 13-year-old daughter to the office. The girl has had intermittent lower abdominal pain, constipation, and difficulty voiding for 3 months. She says that she is not sexually active. She looks well. She has reached age-specific developmental milestones, and her vital signs are within normal range. On abdominal examination, she is found to have a palpable suprapubic mass that persists after voiding. The girl says that her older sister started having menstrual periods at this age. The patient is surprised that hers have not started. Which one of the following is the best next step?
You are caring for a 17-year-old girl who has end-stage renal disease. She is receiving dialysis at the hospital 3 times a week. She requests medical assistance in dying (MAID). Which of the following is the best next step?
A 35-year-old man comes to your office with a history of headaches that last 1 hour and are relieved by 1000 mg of acetaminophen. These headaches, which started 6 months ago after he got his first job as a lawyer, occur regularly. The patient wants a computed tomography scan of his head to rule out a tumour. Physical examination reveals no abnormality. Review of systems does not contribute any positive findings. Which one of the following is the best management?
A 68-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, delirium tremens, and tobacco addiction comes to the Emergency Department with his daughter. She tells you that his behavior has become unmanageable and she feels he may require an increased level of care. His vital signs are:
Blood pressure: 162/105 mm Hg
Heart rate: 112/min, regular
Temperature: 37.8°C
On history, his daughter explains she had to confiscate a half-empty bottle of alcohol from his room yesterday. He is now convinced that there are bugs crawling all over him and he will not relax. He appears pale, sweaty, and shaky. His most recent blood glucose is 7.8 mmol/L (3.8–11.1). Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 43-year-old man comes to your office for the first time. He has not seen a doctor in over 5 years and has no known past medical history. On examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and the remainder of his examination is normal. As part of the initial visit, you order some screening blood work that reveals a fasting blood glucose of 6.3 mmol/L (3.3–5.8) and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.1% (4–6). Which one of the following is the best next step?
Your colleague's receptionist asks you to assess her 4-year-old daughter who has had 2 episodesof acute otitis media in the last month. The mother wants you to arrange a consultation with an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist to get a tympanostomy before her daughter starts school. You do not believe there is a surgical indication at this time. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 62-year-old man, who has not seen a physician in 20 years, presents to your clinic with a burning sensation in his feet. The symptoms have been progressing slowly over the last 6 months. There is no associated motor weakness or skin changes. He reports no significant past medical history and takes no medications. His alcohol intake is minimal. On examination, he has reduced pinprick/vibration sensation and proprioception in the ankles with absent ankle reflexes. Which one of the following blood tests would you expect to be abnormal?
A 56-year-old man is admitted to hospital with pyelonephritis and started on intravenous antibiotics. On day 2 of his hospitalization, he continues to report right flank pain, but he is able to walk. His vital signs are as follows:
Temperature: 38.5°C
Blood pressure: 90/60 mm Hg
Heart rate: 105/min
The patient is mentating well but is concerned about his dog that is home alone due to his unexpected hospitalization. He requests to be released from hospital as he needs to make arrangements for his dog. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A same-sex couple asks to join a family physician’s practice. The physician tells them that shedoes not treat same-sex couples and will refer them to a physician with more clinical experience with same-sex couples. Which one of the following best describes the physician’s obligation under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms?
One of your patients presents to your clinic for a consultation regarding their recurrent hemoptysis. On review of their chart, you realize that although you had ordered chest radiography 2 months ago, the result cannot be found in the chart. You call the radiology department and are relieved to find that the chest radiography was done and that it did not reveal any pathology. After informing the patient of this lapse in reporting, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 58-year-old woman presents with a 1-year history of functional decline. She reports seeing rodents and little children invading her bedroom. Her partner tells you she has a slow, unsteady gait and tends to fall. On examination, she cannot sustain her attention during cognitive testing. Which one of the following is most likely to be found on brain imaging?
A 44-year-old woman presents to the office to discuss contraception. During the gynecologic examination, you notice an anterior cystocele to the hymenal ring. The woman denies any bulge symptoms but does report dribbling of urine, especially when she coughs or jogs.
Which one of the following is the best next step?
An 88-year-old married man is admitted following a cardiac arrest at home. He was not expected to recover, and after 2 weeks, he remains in a coma. His wife states, "I cannot let him go. That would be murder." As the attending physician looking after her husband, which one of the following is the best next course of action?
A 12-year-old boy initially presents with a 4-month history of left knee pain. He denies any obvious history of trauma, but he plays basketball frequently and notes his pain is worse after playing. On physical examination the patient has a prominent tibial tubercle, which is swollen and tender. There is full range of motion in the knee. A radiograph of the left knee reveals an ossicle anterior to the tibial tuberosity. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 1-week-old boy born at full term is brought by his parents to the office with a 2-day history of eye swelling and watery discharge. This morning, the discharge became thick and yellow. On physical exam, he is afebrile and fussy with bilateral eyelid edema, purulent discharge, and erythematous conjunctivae. After taking appropriate cultures of the eyes, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 42-year-old man presents to your clinic for follow-up regarding his anxiety. He lost his job 1 year ago. Since then, he constantly thinks about what happened, trying to understand what went wrong and how he could fix it or prevent it in the future. He is unable to sleep because of this. He has become socially isolated and when he does see friends, he worries constantly that he may say something hurtful. He wishes he could get past what happened and find another job but feels consumed by the fear that he may offend someone in the future. On history, his symptoms did not respond to escitalopram, sertraline, fluvoxamine, or venlafaxine, all at maximum tolerated doses. Which one of the following medications is the most appropriate?
You are following an otherwise healthy 3-month-old girl whose severe bilateral sensorineural deafness was diagnosed after early identification through a universal newborn hearing screening program. She has reached the developmental milestones for her age and has no features of an underlying syndrome. There is no family history of hearing loss. The parents request information on the speech and language prognosis for their daughter. Which one of the following is the most appropriate response?
You are providing medical care to a 78-year-old man and notice a skin lesion which you suspect is malignant melanoma. He has been living in a long-term care facility for 2 years because of incontinence, mobility and vision problems. He is well-liked by facility staff and residents, manages his own affairs and communicates clearly. He has designated his daughter to be his substitute decision-maker and has signed a Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) order. Which one of the following is the best next step in providing care to this patient for his skin lesion?
A 37-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up of his opioid use disorder. He receives opioid agonist treatment, including some take-home doses. At this follow-up visit, he reports some nonprescription opioid use since his last visit. Which one of the following is the best next step?
An 80-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with dizziness. She has a medical history of coronary artery disease. On examination, she is alert and oriented. Her vital signs are as follows:
Her electrocardiogram is shown in the image.
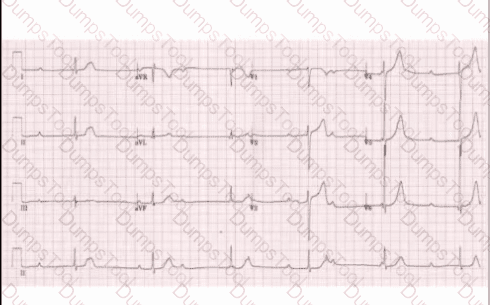
Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Blood pressure
80/60 mm Hg
Heart rate
40/min
Respiratory rate
12/min
Her electrocardiogram is shown in the attached image. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the family practice by her father. The child has a 2-week history of low-grade fever, fatigue, and sore throat. She has also developed several small, round, mildly tender lumps bilaterally in her neck. She was previously well. Which one of the following is most likely to be found on abdominal examination?
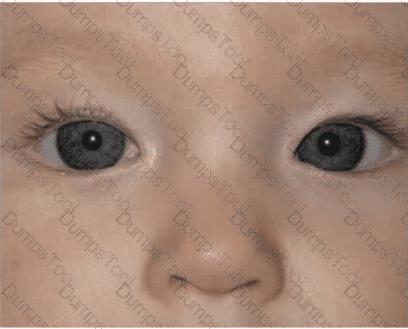
An 18-month-old boy is brought to the office by his guardians for a well-child visit. His guardians are concerned that his eyes do not look the same. On examination, his eyes appear as shown in the referenced photo.
Which one of the following best represents the patient's condition?
A 26-year-old man presents with pain, numbness, and weakness in his right upper extremity. He works as a computer programmer, and his BMI is 32. Symptoms have worsened since he started spending more time on the keyboard. He reports that his right hand feels clumsier while he is typing. Physical examination reveals mild weakness in the intrinsic muscles of that hand, with a positive Tinel sign at the ulnar nerve. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 36-year-old woman presents to the office with a 2-month history of multiple asymptomatic bumps on her vulva. She is not currently sexually active but has had 2 male sexual partners in the past, with the most recent relationship ending 1 year ago. On examination, she appears to have genital warts. She has not received the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine and is not interested in any treatment that is not absolutely necessary. Which of the following is the best next step?
A 14-year-old girl, accompanied by her mother, presents to your office with a 3-month history of feeling "dizzy." After you take an initial history, which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 20-year-old nulligravid woman presents with severe pain during menstruation. She is unable to take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and is adamant about not taking any hormonal therapy. She has questions about non-medicinal therapeutic options. Which one of the following recommendations is the most appropriate?
A 45-year-old woman presents with a 2-week history of a sore left breast. It has become red and swollen. She was previously well, and her menstrual cycles are regular. She has no history of breast cancer, and she has no children. On examination, she has a red, tender, indurated area in her left breast that has only partially responded to oral antibiotics after 10 days. Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 38-year-old marathon runner presents to your office with a 6-month history of increasing right hip pain. The pain is worse with acclivity and has prevented him from running for the last 4 months. He denies fever or chills. His wife adds that she is concerned because he is increasingly disengaged with the family and not interested in other activities he usually enjoys, including sex. Which one of the following is the best next step in management?
You are treating a 78-year-old man for recent onset of diarrhea, tenesmus, and minor bleeding when he wipes. He has a history of prostate cancer that was treated by radiotherapy. Rectal examination findings are normal. Colonoscopy reveals a pale rectum with ulcerations and areas of mucosal hemorrhage. Which one of the following is the most likely explanation for this clinical presentation?
A 72-year-old man reports that his wife says he has hearing trouble. Examination reveals that air conduction on the right side is less than on the left side and greater than bone conduction bilaterally. He hears a tuning fork placed on the top of his head better with his left ear. Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A 31-year-old man presents with nocturnal non-exertional chest pain. During an exercise stress test, he does not experience chest pain, and there are no significant ST segment changes on the electrocardiogram. He achieves 17 metabolic equivalent of task (MET), a blood pressure of 190/96 mm Hg (resting blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg), and a maximum heart rate of 162/min (85% of age-predicted maximum). Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 29-year-old concert pianist with severe chronic kidney disease presents with a 6-month history of loss of appetite and pruritus. Although the issue of initiating dialysis has been discussed with him and his questions answered, he has declined dialysis thus far. You understand his concerns that it will interfere with his concert tour and recording schedule. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 63-year-old woman presents to your office with a history of progressive abdominal discomfort over the past five months. She reports bloating and difficult digestion with constipation. She has no urinary symptoms and denies vaginal or rectal bleeding. An abdominal ultrasound shows a large complex pelvic mass with internal multiloculation and moderate ascites. The cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) is elevated at 1023 U/mL (< 35 U/mL). Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 38-year-old woman presents with diffuse nodularity in the outer upper quadrant of her right breast. There is no obvious dominant mass, nipple discharge, or skin dimpling. There are no palpable lymph nodes. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 47-year-old man presents to the office with a 1-month history of passing blood in his stool 2 to 3 times per week. He is otherwise healthy and denies any systemic symptoms. Other than a small lateral skin tag on digital rectal examination, the physical examination findings are unremarkable. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 62-year-old man (wealthy philanthropist) with emphysema from smoking and a 21-year-old woman (elementary teacher) with cystic fibrosis are both compatible matches for a lung transplant. Which criterion determines organ allocation?
A 55-year-old man presents with vague abdominal pain and general weakness. His mother had colon cancer and died at age 60 years. His physical examination findings and complete blood count results are normal. Which one of the following tests should be ordered first?
A 10-year-old girl is brought to the Emergency Department by her mother because her daughter is crying and says she "can’t pee." Her daughter fell on the monkey bars at school earlier that day. On examination, there is a large vulvar bruise anteriorly. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, aborta 0, presents at 38 weeks' gestation. She is in early labor with ruptured membranes. Her previous pregnancy was complicated by fever during labor. Which one of the following would increase the risk of fever recurrence?
A 27-year-old woman presents with an enlarged thyroid. She had not noticed it herself until her mother brought it to her attention. She is asymptomatic from an endocrine perspective, and her serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is normal.
Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 9-year-old girl from a remote community is brought to the clinic with a 2-week history of swelling in her neck. She has been afebrile but has had some night sweats. On examination, you note a fixed, unilateral, and nontender supraclavicular lymph node measuring 3 cm. The overlying skin color is unremarkable. In addition, you note a slightly enlarged spleen and liver. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 70-year-old man presents with severe, postprandial, mid-abdominal pain which has become more severe over the past 6 to 9 months. It is associated with nausea but has not caused him to vomit or changed his bowel habits. He has lost 14 kg over the last 6 months. Abdominal and rectal examination is normal. Upper gastrointestinal series is unremarkable. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 76-year-old man is brought to the emergency department in an unresponsive state. He has a history of chronic kidney disease with a baseline serum creatinine level of 300 µmol/L (49–93) and a history of dilated cardiomyopathy with an ejection fraction of 30%. On assessment, he has no pulse or blood pressure. Cardiac monitor demonstrates a wide complex tachycardia. Which one of the following recently started medications is the most likely cause of this arrhythmia?
A 53-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a 3-week history of believing his neighbor is poisoning him by pumping gas through his home’s air vent. He appears distracted, irritable, and is speaking very quickly. He has a family history of depression. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
An 80-year-old woman presents to your office with weight loss and generalized weakness. Her husband calls you after the appointment and asks that his wife not be told if she is diagnosed with cancer as hearing this will likely "kill her." Investigations subsequently show that she has metastatic lung cancer. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 26-year-old man presents to your office with fever, chills, and malaise. Aside from an episode of dysuria 8 weeks ago, which spontaneously resolved, he has been healthy. On examination, his left wrist and right ankle are tender. There is a cluster of vesiculopustular lesions on his right hand. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
You are meeting an otherwise healthy 10-year-old boy in your office for the first time. His BMI is at the 80th percentile. He has no symptoms and his physical examination is normal. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 24-year-old man presents to your clinic with a 6-month history of fatigue. On examination, he is pale. His BMI is 16, and his blood pressure is 92/58 mm Hg. Initial laboratory work shows the following:
Creatinine: 64 µmol/L (49–93)
Potassium: 3.0 mmol/L (3.5–5.1)
Sodium: 138 mmol/L (136–146)
TSH: 2.40 mIU/L (0.34–5.60)
CBC: Normal
Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 60-year-old man presents because of a 6-month history of involuntary lip smacking and tongue movements. His medical history is significant for schizophrenia, which has been very stable with haloperidol for the past 20 years. When educating the patient about these particular symptoms, which one of the following statements is accurate?
A 67-year-old man presents to the clinic because of elevated liver enzymes. He is asymptomatic.His medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes, which is being treated with metformin. On physical examination, he looks well. His blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg, his heart rate is 80/min, and his BMI is 35. Findings of the remainder of the examination are normal. His blood work results are as follows:
Platelet count: 170 × 10⁹/L (130–380)
Creatinine: normal
GGT: 75 µmol/L (49–93)
ALT: 146 IU/L (15–85)
AST: 101 IU/L (17–63)
Bilirubin (total): 17 µmol/L (3–17)
INR: 1.2 (0.9–1.2)
Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 40-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with confusion and fever (38.5°C). She has a history of hypothyroidism managed with levothyroxine. Key findings include:
Blood pressure
114/78 mm Hg
Heart rate
85/min
Temperature
38.5°C
Hemoglobin
90 g/L123-157 g/L
Platelet count
25 × 10⁹/L130-400 × 10⁹/L
Peripheral blood film
Schistocytes present
Creatinine
200 μmol/L50-90 μmol/L
A patient's mother comes to you with a prospective cohort study linking autism to the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine. After reviewing the study carefully, you question the results because of problems with the study design and execution. Which one of the following sources of error would be most important in the study design or execution?