Your company runs an enterprise platform on-premises using virtual machines (VMS). Your internet customers have created tens of thousands of DNS domains panting to your public IP addresses allocated to the Vtvls Typically, your customers hard-code your IP addresses In their DNS records You are now planning to migrate the platform to Compute Engine and you want to use Bring your Own IP you want to minimize disruption to the Platform What Should you d0?
You have an application running on Compute Engine that uses BigQuery to generate some results that are stored in Cloud Storage. You want to ensure that none of the application instances have external IP addresses.
Which two methods can you use to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
You have two Google Cloud projects in a perimeter to prevent data exfiltration. You need to move a third project inside the perimeter; however, the move could negatively impact the existing environment. You need to validate the impact of the change. What should you do?
Your organization is developing a landing zone architecture with the following requirements:
There should be no communication between production and non-production environments.
Communication between applications within an environment may be necessary.
Network administrators should centrally manage all network resources, including subnets, routes, and firewall rules.
Each application should be billed separately.
Developers of an application within a project should have the autonomy to create their compute resources.
Up to 1000 applications are expected per environment.
You need to create a design that accommodates these requirements. What should you do?
You need to enable Cloud CDN for all the objects inside a storage bucket. You want to ensure that all the object in the storage bucket can be served by the CDN.
What should you do in the GCP Console?
You have a storage bucket that contains the following objects:
- folder-a/image-a-1.jpg
- folder-a/image-a-2.jpg
- folder-b/image-b-1.jpg
- folder-b/image-b-2.jpg
Cloud CDN is enabled on the storage bucket, and all four objects have been successfully cached. You want to remove the cached copies of all the objects with the prefix folder-a, using the minimum number of commands.
What should you do?
You have deployed a proof-of-concept application by manually placing instances in a single Compute Engine zone. You are now moving the application to production, so you need to increase your application availability and ensure it can autoscale.
How should you provision your instances?
Question:
Your organization has an on-premises data center. You need to provide connectivity from the on-premises data center to Google Cloud. Bandwidth must be at least 1 Gbps, and the traffic must not traverse the internet. What should you do?
Your frontend application VMs and your backend database VMs are all deployed in the same VPC but across different subnets. Global network firewall policy rules are configured to allow traffic from the frontend VMs to the backend VMs. Based on a recent compliance requirement, this traffic must now be inspected by network virtual appliances (NVAs) firewalls that are deployed in the same VPC. The NVAs are configured to be full network proxies and will source NAT-allowed traffic. You need to configure VPC routing to allow the NVAs to inspect the traffic between subnets. What should you do?
You have created an HTTP(S) load balanced service. You need to verify that your backend instances are responding properly.
How should you configure the health check?
You have several microservices running in a private subnet in an existing Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You need to create additional serverless services that use Cloud Run and Cloud Functions to access the microservices. The network traffic volume between your serverless services and private microservices is low. However, each serverless service must be able to communicate with any of your microservices. You want to implement a solution that minimizes cost. What should you do?
Your organization has approximately 100 teams that need to manage their own environments. A central team must manage the network. You need to design a landing zone that provides separate projects for each team. You must also make sure the solution can scale. What should you do?
You are troubleshooting an issue where your organization's Cloud HA VPN is disconnected from your on-premises router for approximately 10 seconds before reestablishing the tunnel. The issue regularly occurs every few hours. You notice that the HA VPN logs show an entry of Received SA_DELETE when this issue occurs. You need to resolve this issue and prevent future VPN downtime from impacting your production applications. What should you do?
Your organization has a hub and spoke architecture with VPC Network Peering, and hybrid connectivity is centralized at the hub. The Cloud Router in the hub VPC is advertising subnet routes, but the on-premises router does not appear to be receiving any subnet routes from the VPC spokes. You need to resolve this issue. What should you do?
(You are developing an internet of things (IoT) application that captures sensor data from multiple devices that have already been set up. You need to identify the global data storage product your company should use to store this data. You must ensure that the storage solution you choose meets your requirements of sub-millisecond latency. What should you do?)
Question:
Your organization has approximately 100 teams that need to manage their own environments. A central team must manage the network. You need to design a landing zone that provides separate projects for each team and ensure the solution can scale. What should you do?
You are creating an instance group and need to create a new health check for HTTP(s) load balancing.
Which two methods can you use to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
Question:
Your organization is developing a landing zone architecture with the following requirements:
No communication between production and non-production environments.
Communication between applications within an environment may be necessary.
Network administrators should centrally manage all network resources, including subnets, routes, and firewall rules.
Each application should be billed separately.
Developers of an application within a project should have the autonomy to create their compute resources.
Up to 1000 applications are expected per environment.
What should you do?
You have configured Cloud CDN using HTTP(S) load balancing as the origin for cacheable content. Compression is configured on the web servers, but responses served by Cloud CDN are not compressed.
What is the most likely cause of the problem?
You want to implement an IPSec tunnel between your on-premises network and a VPC via Cloud VPN. You need to restrict reachability over the tunnel to specific local subnets, and you do not have a device capable of speaking Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Which routing option should you choose?
You are designing a hybrid cloud environment for your organization. Your Google Cloud environment is interconnected with your on-premises network using Cloud HA VPN and Cloud Router. The Cloud Router is configured with the default settings. Your on-premises DNS server is located at 192.168.20.88 and is protected by a firewall, and your Compute Engine resources are located at 10.204.0.0/24. Your Compute Engine resources need to resolve on-premises private hostnames using the domain corp.altostrat.com while still resolving Google Cloud hostnames. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
Your company just completed the acquisition of Altostrat (a current GCP customer). Each company has a separate organization in GCP and has implemented a custom DNS solution. Each organization will retain its current domain and host names until after a full transition and architectural review is done in one year. These are the assumptions for both GCP environments.
• Each organization has enabled full connectivity between all of its projects by using Shared VPC.
• Both organizations strictly use the 10.0.0.0/8 address space for their instances, except for bastion hosts (for accessing the instances) and load balancers for serving web traffic.
• There are no prefix overlaps between the two organizations.
• Both organizations already have firewall rules that allow all inbound and outbound traffic from the 10.0.0.0/8 address space.
• Neither organization has Interconnects to their on-premises environment.
You want to integrate networking and DNS infrastructure of both organizations as quickly as possible and with minimal downtime.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose two.)
In order to provide subnet level isolation, you want to force instance-A in one subnet to route through a security appliance, called instance-B, in another subnet.
What should you do?
Question:
Your organization has a hub and spoke architecture with VPC Network Peering, and hybrid connectivity is centralized at the hub. The Cloud Router in the hub VPC is advertising subnet routes, but the on-premises router does not appear to be receiving any subnet routes from the VPC spokes. You need to resolve this issue. What should you do?
Your company has recently expanded their EMEA-based operations into APAC. Globally distributed users report that their SMTP and IMAP services are slow. Your company requires end-to-end encryption, but you do not have access to the SSL certificates.
Which Google Cloud load balancer should you use?
Your team is developing an application that will be used by consumers all over the world. Currently, the application sits behind a global external application load balancer You need to protect the application from potential application-level attacks. What should you do?
Your organization wants to set up hybrid connectivity with VLAN attachments that terminate in a single Cloud Router with 99.9% uptime. You need to create a network design for your on-premises router that meets those requirements and has an active/passive configuration that uses only one VLAN attachment at a time. What should you do?
You have provisioned a Dedicated Interconnect connection of 20 Gbps with a VLAN attachment of 10 Gbps. You recently noticed a steady increase in ingress traffic on the Interconnect connection from the on-premises data center. You need to ensure that your end users can achieve the full 20 Gbps throughput as quickly as possible. Which two methods can you use to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
Your organization recently re-architected your cloud environment to use Network Connectivity Center. However, an error occurred when you tried to add a new VPC named vpc-dev as a spoke. The error indicated that there was an issue with an existing spoke and the IP space of a VPC named vpc-pre-prod. You must complete the migration quickly and efficiently. What should you do?
(You are managing the security configuration of your company's Google Cloud organization. The Operations team needs specific permissions on both a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster and a Cloud SQL instance. Two predefined Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles exist that contain a subset of the permissions needed by the team. You need to configure the necessary IAM permissions for this team while following Google-recommended practices. What should you do?)
You are using a 10-Gbps direct peering connection to Google together with the gsutil tool to upload files to Cloud Storage buckets from on-premises servers. The on-premises servers are 100 milliseconds away from the Google peering point. You notice that your uploads are not using the full 10-Gbps bandwidth available to you. You want to optimize the bandwidth utilization of the connection.
What should you do on your on-premises servers?
Question:
Your organization has distributed geographic applications with significant data volumes. You need to create a design that exposes the HTTPS workloads globally and keeps traffic costs to a minimum. What should you do?
You have the networking configuration shown in the diagram. A pair of redundant Dedicated Interconnect connections (int-Igal and int-Iga2) terminate on the same Cloud Router. The Interconnect connections terminate on two separate on-premises routers. You are advertising the same prefixes from the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) sessions associated with the Dedicated Interconnect connections. You need to configure one connection as Active for both ingress and egress traffic. If the active Interconnect connection fails, you want the passive Interconnect connection to automatically begin routing all traffic Which two actions should you take to meet this requirement? (Choose Two)
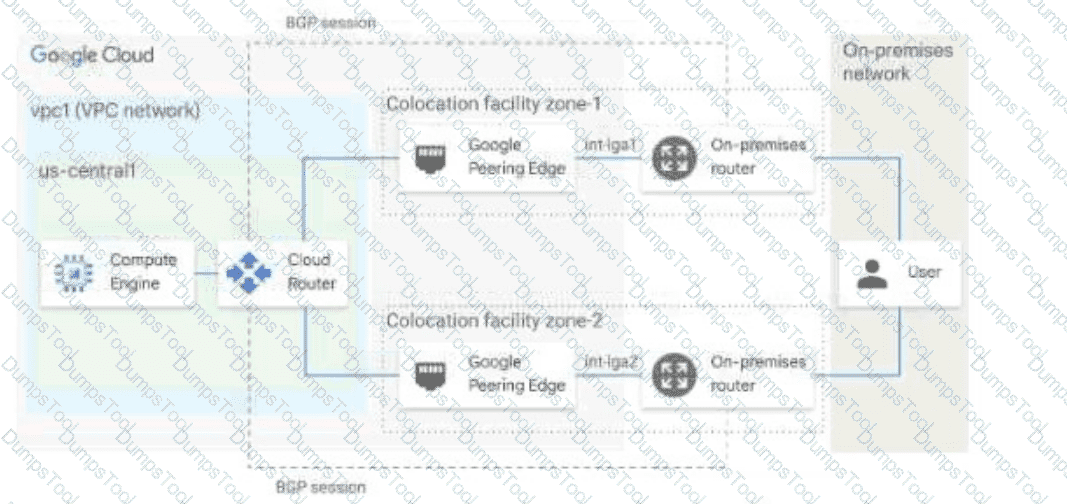
You have provisioned a Partner Interconnect connection to extend connectivity from your on-premises data center to Google Cloud. You need to configure a Cloud Router and create a VLAN attachment to connect to resources inside your VPC. You need to configure an Autonomous System number (ASN) to use with the associated Cloud Router and create the VLAN attachment.
What should you do?
(Your digital media company stores a large number of video files on-premises. Each video file ranges from 100 MB to 100 GB. You are currently storing 150 TB of video data in your on-premises network, with no room for expansion. You need to migrate all infrequently accessed video files older than one year to Cloud Storage to ensure that on-premises storage remains available for new files. You must also minimize costs and control bandwidth usage. What should you do?)
You are configuring an Application Load Balancer. The backend resides in your on-premises data center and is connected by Dedicated Interconnect. You need to ensure the load balancer can reference these on-premises resources. You do not want the traffic to traverse the internet at all. What should you do?
You recently deployed two network virtual appliances in us-central1. Your network appliances provide connectivity to your on-premises network, 10.0.0.0/8. You need to configure the routing for your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Your design must meet the following requirements:
All access to your on-premises network must go through the network virtual appliances.
Allow on-premises access in the event of a single network virtual appliance failure.
Both network virtual appliances must be used simultaneously.
Which method should you use to accomplish this?
You are in the early stages of planning a migration to GCP. You want to test the functionality of your hybrid cloud design before you start to implement it in production. The design includes services running on a Compute Engine Virtual Machine instance that need to communicate to on-premises servers using private IP addresses. The on-premises servers have connectivity to the internet, but you have not yet established any Cloud Interconnect connections. You want to choose the lowest cost method of enabling connectivity between your instance and on-premises servers and complete the test in 24 hours.
Which connectivity method should you choose?
Question:
You are configuring the final elements of a migration effort where resources have been moved from on-premises to Google Cloud. While reviewing the deployed architecture, you noticed that DNS resolution is failing when queries are being sent to the on-premises environment. You log in to a Compute Engine instance, try to resolve an on-premises hostname, and the query fails. DNS queries are not arriving at the on-premises DNS server. You need to use managed services to reconfigure Cloud DNS to resolve the DNS error. What should you do?
You created a VPC network named Retail in auto mode. You want to create a VPC network named Distribution and peer it with the Retail VPC.
How should you configure the Distribution VPC?
You need to create a GKE cluster in an existing VPC that is accessible from on-premises. You must meet the following requirements:
IP ranges for pods and services must be as small as possible.
The nodes and the master must not be reachable from the internet.
You must be able to use kubectl commands from on-premises subnets to manage the cluster.
How should you create the GKE cluster?
You have a web application that is currently hosted in the us-central1 region. Users experience high latency when traveling in Asia. You've configured a network load balancer, but users have not experienced a performance improvement. You want to decrease the latency.
What should you do?
You are implementing a VPC architecture for your organization by using a Network Connectivity Center hub and spoke topology:
• There is one Network Connectivity Center hybrid spoke to receive on-premises routes.
• There is one VPC spoke that needs to be added as a Network Connectivity Center spoke.
Your organization has limited routable IP space fortheir cloud environment (192.168.0.0/20). The Network Connectivity Center spoke VPC is connected to on-premises with a Cloud Interconnect connection in the us-east4 region. The on-premises IP range is 172.16.0.0/16. You need to reach on-premises resources from multiple Google Cloud regions (us-westl, europe-centrall, and asia-southeastl) and minimize the IP addresses being used. What should you do?
Question:
Your company's current network architecture has three VPC Service Controls perimeters:
One perimeter (PERIMETER_PROD) to protect production storage buckets
One perimeter (PERIMETER_NONPROD) to protect non-production storage buckets
One perimeter (PERIMETER_VPC) that contains a single VPC (VPC_ONE)
In this single VPC (VPC_ONE), the IP_RANGE_PROD is dedicated to the subnets of the production workloads, and the IP_RANGE_NONPROD is dedicated to subnets of non-production workloads. Workloads cannot be created outside those two ranges. You need to ensure that production workloads can access only production storage buckets and non-production workloads can access only non-production storage buckets with minimal setup effort. What should you do?
Question:
Your organization recently exposed a set of services through a global external Application Load Balancer. After conducting some testing, you observed that responses would intermittently yield a non-HTTP 200 response. You need to identify the error. What should you do? (Choose 2 answers)
You need to configure a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. The initial deployment should have 5 nodes with the potential to scale to 10 nodes. The maximum number of Pods per node is 8. The number of services could grow from 100 to up to 1024. How should you design the IP schema to optimally meet this requirement?
You are using the gcloud command line tool to create a new custom role in a project by coping a predefined role. You receive this error message:
INVALID_ARGUMENT: Permission resourcemanager.projects.list is not valid
What should you do?
Your company has a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with two Dedicated Interconnect connections in two different regions: us-west1 and us-east1. Each Dedicated Interconnect connection is attached to a Cloud Router in its respective region by a VLAN attachment. You need to configure a high availability failover path. By default, all ingress traffic from the on-premises environment should flow to the VPC using the us-west1 connection. If us-west1 is unavailable, you want traffic to be rerouted to us-east1. How should you configure the multi-exit discriminator (MED) values to enable this failover path?
You need to configure a static route to an on-premises resource behind a Cloud VPN gateway that is configured for policy-based routing using the gcloud command.
Which next hop should you choose?
You want Cloud CDN to serve the https://www.example.com/images/spacetime.png static image file that is hosted in a private Cloud Storage bucket, You are using the VSE ORIG.-X_NZADERS cache mode You receive an HTTP 403 error when opening the file In your browser and you see that the HTTP response has a Cache-control: private, max-age=O header How should you correct this Issue?
You need to centralize the Identity and Access Management permissions and email distribution for the WebServices Team as efficiently as possible.
What should you do?
You are deploying a global external TCP load balancing solution and want to preserve the source IP address of the original layer 3 payload.
Which type of load balancer should you use?
Your company has recently installed a Cloud VPN tunnel between your on-premises data center and your Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You need to configure access to the Cloud Functions API for your on-premises servers. The configuration must meet the following requirements:
Certain data must stay in the project where it is stored and not be exfiltrated to other projects.
Traffic from servers in your data center with RFC 1918 addresses do not use the internet to access Google Cloud APIs.
All DNS resolution must be done on-premises.
The solution should only provide access to APIs that are compatible with VPC Service Controls.
What should you do?
You have deployed a new internal application that provides HTTP and TFTP services to on-premises hosts. You want to be able to distribute traffic across multiple Compute Engine instances, but need to ensure that clients are sticky to a particular instance across both services.
Which session affinity should you choose?
You are increasing your usage of Cloud VPN between on-premises and GCP, and you want to support more traffic than a single tunnel can handle. You want to increase the available bandwidth using Cloud VPN.
What should you do?
You have an application hosted on a Compute Engine virtual machine instance that cannot communicate with a resource outside of its subnet. When you review the flow and firewall logs, you do not see any denied traffic listed.
During troubleshooting you find:
• Flow logs are enabled for the VPC subnet, and all firewall rules are set to log.
• The subnetwork logs are not excluded from Stackdriver.
• The instance that is hosting the application can communicate outside the subnet.
• Other instances within the subnet can communicate outside the subnet.
• The external resource initiates communication.
What is the most likely cause of the missing log lines?
You are the Organization Admin for your company. One of your engineers is responsible for setting up multiple host projects across multiple folders and sharing subnets with service projects. You need to enable the engineer's Identity and Access Management (IAM) configuration to complete their task in the fewest number of steps. What should you do?
Your company is running out of network capacity to run a critical application in the on-premises data center. You want to migrate the application to GCP. You also want to ensure that the Security team does not lose their ability to monitor traffic to and from Compute Engine instances.
Which two products should you incorporate into the solution? (Choose two.)
You have configured a Compute Engine virtual machine instance as a NAT gateway. You execute the following command:
gcloud compute routes create no-ip-internet-route \
--network custom-network1 \
--destination-range 0.0.0.0/0 \
--next-hop instance nat-gateway \
--next-hop instance-zone us-central1-a \
--tags no-ip --priority 800
You want existing instances to use the new NAT gateway. Which command should you execute?
In your Google Cloud organization, you have two folders: Dev and Prod. You want a scalable and consistent way to enforce the following firewall rules for all virtual machines (VMs) with minimal cost:
Port 8080 should always be open for VMs in the projects in the Dev folder.
Any traffic to port 8080 should be denied for all VMs in your projects in the Prod folder.
What should you do?
All the instances in your project are configured with the custom metadata enable-oslogin value set to FALSE and to block project-wide SSH keys. None of the instances are set with any SSH key, and no project-wide SSH keys have been configured. Firewall rules are set up to allow SSH sessions from any IP address range. You want to SSH into one instance.
What should you do?
You are adding steps to a working automation that uses a service account to authenticate. You need to drive the automation the ability to retrieve files from a Cloud Storage bucket. Your organization requires using the least privilege possible.
What should you do?
Your company is planning a migration to Google Kubernetes Engine. Your application team informed you that they require a minimum of 60 Pods per node and a maximum of 100 Pods per node Which Pod per node CIDR range should you use?
You have just deployed your infrastructure on Google Cloud. You now need to configure the DNS to meet the following requirements:
Your on-premises resources should resolve your Google Cloud zones.
Your Google Cloud resources should resolve your on-premises zones.
You need the ability to resolve “. internal” zones provisioned by Google Cloud.
What should you do?