Which of the following is a program of the Food and Drug Administration FDA post market surveillance system for medical devices that requires healthcare facilities to report patient deaths or injuries related to a medical device?
Which of the following are common techniques used to include patients and families in programs to educate patients about their safety?
lay persons on select committees
patient education opportunities
patient events referred for peer review
event reporting by patients and families
What is one advantage of avoluntaryerror reporting system over amandatoryerror reporting system?
Which type of information was associated with the former HIPDB (now within NPDB) but not the original NPDB focus?
In enterprise risk management, which of the following are external factors that may affect risk?
An interrogatory requests insurance policy information. A risk manager should
According to The Joint Commission, which of the following should be done to patient-owned electrical devices entering the facility?
What factors are included in a calculation of Risk Priority Number (RPN) in FMEA?
Which of the following wouldnotbe considered an emergency condition for EMTALA purposes (as a general example set)?
What is the voluntary relinquishment by the insurer or self-insurer of the right to recover from a third party?
For a liability claim to succeed, the claimant must establish duty owed, duty breached, proximate cause, and
Per The Joint Commission and CMS patient visitation standards, a hospital may restrict an individual's ability to visit a patient if the visitor
The Joint Commission requires that after a healthcare organization becomes aware of a sentinel event, it must complete a root cause analysis and action plan within how many days?
A hospital's Ethics Committee is seeking advice on a case involving the elective sterilization of an adolescent patient who is developmentally disabled. One of the parents is refusing consent. The risk manager should evaluate which of the following?
who has consent authority
competency level of the patient
diagnosis of the patient
state statutes and laws
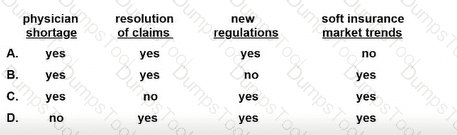
When considering the proper insurance to purchase for an organization and its practitioners, a risk manager should understand which of the following about specific types of coverage?
Which of the following isnotone of the patient rights enumerated in the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA)?
What group reports information (historically HIPDB content; now within NPDB) related to fraud/abuse oversight?
All of the following are valid reasons for performing risk management review of policies and procedures EXCEPT
An organization's chief of orthopedics has scheduled an implant of a new artificial hip for the next day. The chief developed the artificial hip while working as a consultant for a medical device company. The device has not yet been approved by the FDA or the Institutional Review Board. The risk manager's best immediate course of action is to
When a hospital notes that most errors are occurring at the “sharp end,” what does that mean?
A healthcare entity has a large fleet of vehicles driven by employees. What is the minimum required documentation the entity should obtain for each driver on an annual basis?
Who are most likelynotto report errors in typical incident reporting systems?