Which of the following results in the most devastating business interruptions?
Loss of Hardware/Software
Loss of Data
Loss of Communication Links
Loss of Applications
Source: Veritas eLearning CD - Introducing Disaster Recovery Planning, Chapter 1.
All of the others can be replaced or repaired. Data that is lost and was not backed up, cannot be restored.
Which of the following categories of hackers poses the greatest threat?
Disgruntled employees
Student hackers
Criminal hackers
Corporate spies
According to the authors, hackers fall in these categories, in increasing threat order: security experts, students, underemployed adults, criminal hackers, corporate spies and disgruntled employees.
Disgruntled employees are the most dangerous security problem of all because they are most likely to have a good knowledge of the organization's IT systems and security measures.
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 2: Hackers.
Who should direct short-term recovery actions immediately following a disaster?
Chief Information Officer.
Chief Operating Officer.
Disaster Recovery Manager.
Chief Executive Officer.
The Disaster Recovery Manager should also be a member of the team that assisted in the development of the Disaster Recovery Plan. Senior-level management need to support the process but would not be involved with the initial process.
The following answers are incorrect:
Chief Information Officer. Is incorrect because the Senior-level management are the ones to authorize the recovery plan and process but during the initial recovery process they will most likely be heavily involved in other matters.
Chief Operating Officer. Is incorrect because the Senior-level management are the ones to authorize the recovery plan and process but during the initial recovery process they will most likely be heavily involved in other matters.
Chief Executive Officer. Is incorrect because the Senior-level management are the ones to authorize the recovery plan and process but during the initial recovery process they will most likely be heavily involved in other matters.
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is what type of control?
A preventive control.
A detective control.
A recovery control.
A directive control.
These controls can be used to investigate what happen after the fact. Your IDS may collect information on where the attack came from, what port was use, and other details that could be used in the investigation steps.
"Preventative control" is incorrect. Preventative controls preclude events or actions that might compromise a system or cause a policy violation. An intrusion prevention system would be an example of a preventative control.
"Recovery control" is incorrect. Recover controls include processes used to return the system to a secure state after the occurrence of a security incident. Backups and redundant components are examples of recovery controls.
"Directive controls" is incorrect. Directive controls are administrative instruments such as policies, procedures, guidelines, and aggreements. An acceptable use policy is an example of a directive control.
References:
CBK, pp. 646 - 647
Which of the following is a large hardware/software backup system that uses the RAID technology?
Tape Array.
Scale Array.
Crimson Array
Table Array.
A Tape Array is a large hardware/software backup system based on the RAID technology.
There is a misconception that RAID can only be used with Disks.
All large storage vendor from HP, to EMC, to Compaq have Tape Array based on RAID technology they offer.
This is a VERY common type of storage at an affordable price as well.
So RAID is not exclusively for DISKS. Often time this is referred to as Tape Librairies or simply RAIT.
RAIT (redundant array of independent tapes) is similar to RAID, but uses tape drives instead of disk drives. Tape storage is the lowest-cost option for very large amounts of data, but is very slow compared to disk storage. As in RAID 1 striping, in RAIT, data are striped in parallel to multiple tape drives, with or without a redundant parity drive. This provides the high capacity at low cost typical of tape storage, with higher-than-usual tape data transfer rates and optional data integrity.
References:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 70.
and
Harris, Shon (2012-10-18). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 1271). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
What is the 802.11 standard related to?
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Wireless network communications
Packet-switching technology
The OSI/ISO model
The 802.11 standard outlines how wireless clients and APs communicate, lays out the specifications of their interfaces, dictates how signal transmission should take place, and describes how authentication, association, and security should be implemeted.
The following answers are incorrect:
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Public Key Infrastructure is a supporting infrastructure to manage public keys. It is not part of the IEEE 802 Working Group standard.
Packet-switching technology A packet-switching technology is not included in the IEEE 802 Working Group standard. It is a technology where-in messages are broken up into packets, which then travel along different routes to the destination.
The OSI/ISO model The Open System Interconnect model is a sevel-layer model defined as an international standard describing network communications.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
Source: Shon Harris - "All-in-One CISSP Exam Guide" Fourth Edition; Chapter 7 - Telecommunications and Network Security: pg. 624.
802.11 refers to a family of specifications developed by the IEEE for Wireless LAN technology. 802.11 specifies an over-the-air interface between a wireless client and a base station or between two wireless clients. The IEEE accepted the specification in 1997. There are several specifications in the 802.11 family:
802.11 # applies to wireless LANs and provides 1 or 2 Mbps transmission in the 2.4 GHz band using either frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) or direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS).
802.11a # an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LANs and provides up to 54 Mbps in the 5GHz band. 802.11a uses an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing encoding scheme rather than FHSS or DSSS.
802.11b (also referred to as 802.11 High Rate or Wi-Fi) # an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LANS and provides 11 Mbps transmission (with a fallback to 5.5, 2 and 1 Mbps) in the 2.4 GHz band. 802.11b uses only DSSS. 802.11b was a 1999 ratification to the original 802.11 standard, allowing wireless functionality comparable to Ethernet.
802.11g # applies to wireless LANs and provides 20+ Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band.
Source: 802.11 Planet's web site.
A proxy is considered a:
first generation firewall.
third generation firewall.
second generation firewall.
fourth generation firewall.
The proxy (application layer firewall, circuit level proxy, or application proxy ) is a second generation firewall
"First generation firewall" incorrect. A packet filtering firewall is a first generation firewall.
"Third generation firewall" is incorrect. Stateful Firewall are considered third generation firewalls
"Fourth generation firewall" is incorrect. Dynamic packet filtering firewalls are fourth generation firewalls
References:
CBK, p. 464
AIO3, pp. 482 - 484
Neither CBK or AIO3 use the generation terminology for firewall types but you will encounter it frequently as a practicing security professional. See http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/iaabu/centri4/user/scf4ch3.htm for a general discussion of the different generations.
Which backup method only copies files that have been recently added or changed and also leaves the archive bit unchanged?
Full backup method
Incremental backup method
Fast backup method
Differential backup method
A differential backup is a partial backup that copies a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on, indicating that it has changed since the last full backup. A differential backup leaves the archive bits unchanged on the files it copies.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 69).
Also see: http://e-articles.info/e/a/title/Backup-Types/
Backup software can use or ignore the archive bit in determining which files to back up, and can either turn the archive bit off or leave it unchanged when the backup is complete. How the archive bit is used and manipulated determines what type of backup is done, as follows
Full backup
A full backup, which Microsoft calls a normal backup, backs up every selected file, regardless of the status of the archive bit. When the backup completes, the backup software turns off the archive bit for every file that was backed up. Note that "full" is a misnomer because a full backup backs up only the files you have selected, which may be as little as one directory or even a single file, so in that sense Microsoft's terminology is actually more accurate. Given the choice, full backup is the method to use because all files are on one tape, which makes it much easier to retrieve files from tape when necessary. Relative to partial backups, full backups also increase redundancy because all files are on all tapes. That means that if one tape fails, you may still be able to retrieve a given file from another tape.
Differential backup
A differential backup is a partial backup that copies a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on, indicating that it has changed since the last full backup. A differential backup leaves the archive bits unchanged on the files it copies. Accordingly, any differential backup set contains all files that have changed since the last full backup. A differential backup set run soon after a full backup will contain relatively few files. One run soon before the next full backup is due will contain many files, including those contained on all previous differential backup sets since the last full backup. When you use differential backup, a complete backup set comprises only two tapes or tape sets: the tape that contains the last full backup and the tape that contains the most recent differential backup.
Incremental backup
An incremental backup is another form of partial backup. Like differential backups, Incremental Backups copy a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on. Unlike the differential backup, however, the incremental backup clears the archive bits for the files it backs up. An incremental backup set therefore contains only files that have changed since the last full backup or the last incremental backup. If you run an incremental backup daily, files changed on Monday are on the Monday tape, files changed on Tuesday are on the Tuesday tape, and so forth. When you use an incremental backup scheme, a complete backup set comprises the tape that contains the last full backup and all of the tapes that contain every incremental backup done since the last normal backup. The only advantages of incremental backups are that they minimize backup time and keep multiple versions of files that change frequently. The disadvantages are that backed-up files are scattered across multiple tapes, making it difficult to locate any particular file you need to restore, and that there is no redundancy. That is, each file is stored only on one tape.
Full copy backup
A full copy backup (which Microsoft calls a copy backup) is identical to a full backup except for the last step. The full backup finishes by turning off the archive bit on all files that have been backed up. The full copy backup instead leaves the archive bits unchanged. The full copy backup is useful only if you are using a combination of full backups and incremental or differential partial backups. The full copy backup allows you to make a duplicate "full" backup—e.g., for storage offsite, without altering the state of the hard drive you are backing up, which would destroy the integrity of the partial backup rotation.
Some Microsoft backup software provides a bizarre backup method Microsoft calls a daily copy backup. This method ignores the archive bit entirely and instead depends on the date- and timestamp of files to determine which files should be backed up. The problem is, it's quite possible for software to change a file without changing the date- and timestamp, or to change the date- and timestamp without changing the contents of the file. For this reason, we regard the daily copy backup as entirely unreliable and recommend you avoid using it.
What can best be defined as the detailed examination and testing of the security features of an IT system or product to ensure that they work correctly and effectively and do not show any logical vulnerabilities, such as evaluation criteria?
Acceptance testing
Evaluation
Certification
Accreditation
Evaluation as a general term is described as the process of independently assessing a system against a standard of comparison, such as evaluation criteria. Evaluation criterias are defined as a benchmark, standard, or yardstick against which accomplishment, conformance, performance, and suitability of an individual, hardware, software, product, or plan, as well as of risk-reward ratio is measured.
What is computer security evaluation?
Computer security evaluation is the detailed examination and testing of the security features of an IT system or product to ensure that they work correctly and effectively and do not show any logical vulnerabilities. The Security Target determines the scope of the evaluation. It includes a claimed level of Assurance that determines how rigorous the evaluation is.
Criteria
Criteria are the "standards" against which security evaluation is carried out. They define several degrees of rigour for the testing and the levels of assurance that each confers. They also define the formal requirements needed for a product (or system) to meet each Assurance level.
TCSEC
The US Department of Defense published the first criteria in 1983 as the Trusted Computer Security Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC), more popularly known as the "Orange Book". The current issue is dated 1985. The US Federal Criteria were drafted in the early 1990s as a possible replacement but were never formally adopted.
ITSEC
During the 1980s, the United Kingdom, Germany, France and the Netherlands produced versions of their own national criteria. These were harmonised and published as the Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC). The current issue, Version 1.2, was published by the European Commission in June 1991. In September 1993, it was followed by the IT Security Evaluation Manual (ITSEM) which specifies the methodology to be followed when carrying out ITSEC evaluations.
Common Criteria
The Common Criteria represents the outcome of international efforts to align and develop the existing European and North American criteria. The Common Criteria project harmonises ITSEC, CTCPEC (Canadian Criteria) and US Federal Criteria (FC) into the Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC) for use in evaluating products and systems and for stating security requirements in a standardised way. Increasingly it is replacing national and regional criteria with a worldwide set accepted by the International Standards Organisation (ISO15408).
The following answer were not applicable:
Certification is the process of performing a comprehensive analysis of the security features and safeguards of a system to establish the extent to which the security requirements are satisfied. Shon Harris states in her book that Certification is the comprehensive technical evaluation of the security components and their compliance for the purpose of accreditation.
Wikipedia describes it as: Certification is a comprehensive evaluation of the technical and non-technical security controls (safeguards) of an information system to support the accreditation process that establishes the extent to which a particular design and implementation meets a set of specified security requirements
Accreditation is the official management decision to operate a system. Accreditation is the formal declaration by a senior agency official (Designated Accrediting Authority (DAA) or Principal Accrediting Authority (PAA)) that an information system is approved to operate at an acceptable level of risk, based on the implementation of an approved set of technical, managerial, and procedural security controls (safeguards).
Acceptance testing refers to user testing of a system before accepting delivery.
Reference(s) used for this question:
HARE, Chris, Security Architecture and Models, Area 6 CISSP Open Study Guide, January 2002.
and
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Certification_and_Accreditation
and
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/evaluation-criteria.html
and
http://www.cesg.gov.uk/products_services/iacs/cc_and_itsec/secevalcriteria.shtml
The fact that a network-based IDS reviews packets payload and headers enable which of the following?
Detection of denial of service
Detection of all viruses
Detection of data corruption
Detection of all password guessing attacks
Because a network-based IDS reviews packets and headers, denial of service attacks can also be detected.
This question is an easy question if you go through the process of elimination. When you see an answer containing the keyword: ALL It is something a give away that it is not the proper answer. On the real exam you may encounter a few question where the use of the work ALL renders the choice invalid. Pay close attention to such keyword.
The following are incorrect answers:
Even though most IDSs can detect some viruses and some password guessing attacks, they cannot detect ALL viruses or ALL password guessing attacks. Therefore these two answers are only detractors.
Unless the IDS knows the valid values for a certain dataset, it can NOT detect data corruption.
Reference used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
A momentary low voltage, from 1 cycle to a few seconds, is a:
spike
blackout
sag
fault
A momentary low voltage is a sag. A synonym would be a dip.
Risks to electrical power supply:
POWER FAILURE
Blackout: complete loss of electrical power
Fault: momentary power outage
POWER DEGRADATION
Brownout: an intentional reduction of voltage by the power company.
Sag/dip: a short period of low voltage
POWER EXCESS
Surge: Prolonged rise in voltage
Spike: Momentary High Voltage
In-rush current: the initial surge of current required by a load before it reaches normal operation.
– Transient: line noise or disturbance is superimposed on the supply circuit and can cause fluctuations in electrical power
Refence(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 462). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following statements regarding an off-site information processing facility is TRUE?
It should have the same amount of physical access restrictions as the primary processing site.
It should be located in proximity to the originating site so that it can quickly be made operational.
It should be easily identified from the outside so in the event of an emergency it can be easily found.
Need not have the same level of environmental monitoring as the originating site since this would be cost prohibitive.
It is very important that the offsite has the same restrictions in order to avoide misuse.
The following answers are incorrect because:
It should be located in proximity to the originating site so that it can quickly be made operational is incorrect as the offsite is also subject to the same disaster as of the primary site.
It should be easily identified from the outside so in the event of an emergency it can be easily found is also incorrect as it should not be easily identified to prevent intentional sabotage.
Need not have the same level of environmental monitoring as the originating site since this would be cost prohibitive is also incorrect as it should be like its primary site.
Reference : Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, chapter 5: Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (page 265).
Configuration Management controls what?
Auditing of changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
Control of changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
Changes in the configuration access to the Trusted Computing Base.
Auditing and controlling any changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
All of these are components of Configuration Management.
The following answers are incorrect:
Auditing of changes to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because it refers only to auditing the changes, but nothing about controlling them.
Control of changes to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because it refers only to controlling the changes, but nothing about ensuring the changes will not lead to a weakness or fault in the system.
Changes in the configuration access to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because this does not refer to controlling the changes or ensuring the changes will not lead to a weakness or fault in the system.
Which expert system operating mode allows determining if a given hypothesis is valid?
Blackboard
Lateral chaining
Forward chaining
Backward chaining
Backward-chaining mode - the expert system backtracks to determine if a given hypothesis is valid. Backward-chaining is generally used when there are a large number of possible solutions relative to the number of inputs.
Incorrect answers are:
In a forward-chaining mode, the expert system acquires information and comes to a conclusion based on that information. Forward-chaining is the reasoning approach that can be used when there is a small number of solutions relative to the number of inputs.
Blackboard is an expert system-reasoning methodology in which a solution is generated by the use of a virtual blackboard, wherein information or potential solutions are placed on the blackboard by a plurality of individuals or expert knowledge sources. As more information is placed on the blackboard in an iterative process, a solution is generated.
Lateral-chaining mode - No such expert system mode.
Sources:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 7: Applications and Systems Development (page 259).
KRUTZ, Ronald & VINES, Russel, The CISSP Prep Guide: Gold Edition, Wiley Publishing Inc., 2003, Chapter 7: Expert Systems (page 354).
What is defined as the rules for communicating between computers on a Local Area Network (LAN)?
LAN Media Access methods
LAN topologies
LAN transmission methods
Contention Access Control
Media contention occurs when two or more network devices have data to send at the same time. Because multiple devices cannot talk on the network simultaneously, some type of method must be used to allow one device access to the network media at a time.
This is done in two main ways: carrier sense multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD) and token passing.
In networks using CSMA/CD technology such as Ethernet, network devices contend for the network media. When a device has data to send, it first listens to see if any other device is currently using the network. If not, it starts sending its data. After finishing its transmission, it listens again to see if a collision occurred. A collision occurs when two devices send data simultaneously. When a collision happens, each device waits a random length of time before resending its data. In most cases, a collision will not occur again between the two devices. Because of this type of network contention, the busier a network becomes, the more collisions occur. This is why performance of Ethernet degrades rapidly as the number of devices on a single network increases.
In token-passing networks such as Token Ring and FDDI, a special network frame called a token is passed around the network from device to device. When a device has data to send, it must wait until it has the token and then sends its data. When the data transmission is complete, the token is released so that other devices may use the network media. The main advantage of token-passing networks is that they are deterministic. In other words, it is easy to calculate the maximum time that will pass before a device has the opportunity to send data. This explains the popularity of token-passing networks in some real-time environments such as factories, where machinery must be capable of communicating at a determinable interval.
For CSMA/CD networks, switches segment the network into multiple collision domains. This reduces the number of devices per network segment that must contend for the media. By creating smaller collision domains, the performance of a network can be increased significantly without requiring addressing changes.
The following are incorrect answers:
LAN topologies: Think of a topology as a network's virtual shape or structure. This shape does not necessarily correspond to the actual physical layout of the devices on the network. For example, the computers on a home LAN may be arranged in a circle in a family room, but it would be highly unlikely to find a ring topology there. Common topologies are: bus, ring, star or meshed. See THIS LINK for more information.
LAN transmission methods: refer to the way packets are sent on the network and are either unicast, multicast or broadcast. See THIS LINK for more information.
Contention Access Control: This is a bogus detractor.
Contention is a real term but Contention Access Control is just made up. Contention methods is very closely related to Media Access Control methods. In communication networks, contention is a media access method that is used to share a broadcast medium. In contention, any computer in the network can transmit data at any time (first come-first served). This system breaks down when two computers attempt to transmit at the same time. This is a case of collision. To avoid collision, carrier sensing mechanism is used. Here each computer listens to the network before attempting to transmit. If the network is busy, it waits until network quiets down. In carrier detection, computers continue to listen to the network as they transmit. If computer detects another signal that interferes with the signal it is sending, it stops transmitting. Both computers then wait for random amount of time and attempt to transmit. Contention methods are most popular media access control method on LANs.
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/Introduction_to_LAN_Protocols#LAN_Media-Access_Methods
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contention_%28telecommunications%29
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) provides some of the services of Authentication Headers (AH), but it is primarily designed to provide:
Confidentiality
Cryptography
Digital signatures
Access Control
Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, MICKI, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th Edition, Volume 2, 2001, CRC Press, NY, page 164.
Secure Shell (SSH) is a strong method of performing:
client authentication
server authentication
host authentication
guest authentication
Secure shell (SSH) was designed as an alternative to some of the insecure protocols and allows users to securely access resources on remote computers over an encrypted tunnel. The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a protocol for secure remote login and other secure network services over an insecure network. The SSH authentication protocol runs on top of the SSH transport layer protocol and provides a single authenticated tunnel for the SSH connection protocol.
SSH’s services include remote log-on, file transfer, and command execution. It also supports port forwarding, which redirects other protocols through an encrypted SSH tunnel. Many users protect less secure traffic of protocols, such as X Windows and VNC (virtual network computing), by forwarding them through a SSH tunnel.
The SSH tunnel protects the integrity of communication, preventing session hijacking and other man-in-the-middle attacks. Another advantage of SSH over its predecessors is that it supports strong authentication. There are several alternatives for SSH clients to authenticate to a SSH server, including passwords and digital certificates.
Keep in mind that authenticating with a password is still a significant improvement over the other protocols because the password is transmitted encrypted.
There are two incompatible versions of the protocol, SSH-1 and SSH-2, though many servers support both. SSH-2 has improved integrity checks (SSH-1 is vulnerable to an insertion attack due to weak CRC-32 integrity checking) and supports local extensions and additional types of digital certificates such as Open PGP. SSH was originally designed for UNIX, but there are now implementations for other operating systems, including Windows, Macintosh, and OpenVMS.
Is SSH 3.0 the same as SSH3?
The short answer is: NO SSH 3.0 refers to version 3 of SSH Communications SSH2 protocol implementation and it could also refer to OpenSSH Version 3.0 of its SSH2 software. The "3" refers to the software release version not the protocol version. As of this writing (July 2013), there is no SSH3 protocol.
"Server authentication" is incorrect. Though many SSH clients allow pre-caching of server/host keys, this is a minimal form of server/host authentication.
"Host authentication" is incorrect. Though many SSH clients allow pre-caching of server/host keys, this is a minimal form of server/host authentication.
"Guest authentication" is incorrect. The general idea of "guest" is that it is unauthenticated access.
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4252.txt
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 7080-7088). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following is an IP address that is private (i.e. reserved for internal networks, and not a valid address to use on the Internet)?
172.12.42.5
172.140.42.5
172.31.42.5
172.15.42.5
This is a valid Class B reserved address. For Class B networks, the reserved addresses are 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255.
The private IP address ranges are defined within RFC 1918:
RFC 1918 private ip address range

The following answers are incorrect:
172.12.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class B reserved address.
172.140.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class B reserved address.
172.15.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class B reserved address.
The Logical Link Control sub-layer is a part of which of the following?
The ISO/OSI Data Link layer
The Reference monitor
The Transport layer of the TCP/IP stack model
Change management control
The OSI/ISO Data Link layer is made up of two sub-layers; (1) the Media Access Control layer refers downward to lower layer hardware functions and (2) the Logical Link Control refers upward to higher layer software functions. Other choices are distracters.
Source: ROTHKE, Ben, CISSP CBK Review presentation on domain 2, August 1999.
Which type of firewall can be used to track connectionless protocols such as UDP and RPC?
Stateful inspection firewalls
Packet filtering firewalls
Application level firewalls
Circuit level firewalls
Packets in a stateful inspection firewall are queued and then analyzed at all OSI layers, providing a more complete inspection of the data. By examining the state and context of the incoming data packets, it helps to track the protocols that are considered "connectionless", such as UDP-based applications and Remote Procedure Calls (RPC).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 91).
Which of the following statements pertaining to PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is incorrect?
PPTP allow the tunnelling of any protocols that can be carried within PPP.
PPTP does not provide strong encryption.
PPTP does not support any token-based authentication method for users.
PPTP is derived from L2TP.
PPTP is an encapsulation protocol based on PPP that works at OSI layer 2 (Data Link) and that enables a single point-to-point connection, usually between a client and a server.
While PPTP depends on IP to establish its connection.
As currently implemented, PPTP encapsulates PPP packets using a modified version of the generic routing encapsulation (GRE) protocol, which gives PPTP to the flexibility of handling protocols other than IP, such as IPX and NETBEUI over IP networks.
PPTP does have some limitations:
It does not provide strong encryption for protecting data, nor does it support any token-based methods for authenticating users.
L2TP is derived from L2F and PPTP, not the opposite.
What is called the access protection system that limits connections by calling back the number of a previously authorized location?
Sendback systems
Callback forward systems
Callback systems
Sendback forward systems
The Answer: Call back Systems; Callback systems provide access protection by calling back the number of a previously authorized location, but this control can be compromised by call forwarding.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 35.
A DMZ is also known as a
screened subnet
three legged firewall
a place to attract hackers
bastion host
This is another name for the demilitarized zone (DMZ) of a network.
"Three legged firewall" is incorrect. While a DMZ can be implemented on one leg of such a device, this is not the best answer.
"A place to attract hackers" is incorrect. The DMZ is a way to provide limited public access to an organization's internal resources (DNS, EMAIL, public web, etc) not as an attractant for hackers.
"Bastion host" is incorrect. A bastion host serves as a gateway between trusted and untrusted network.
References:
CBK, p. 434
AIO3, pp. 495 - 496
What is the main issue with media reuse?
Degaussing
Data remanence
Media destruction
Purging
The main issue with media reuse is data remanence, where residual information still resides on a media that has been erased. Degaussing, purging and destruction are ways to handle media that contains data that is no longer needed or used.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#10 Physical Security (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 5).
Which conceptual approach to intrusion detection system is the most common?
Behavior-based intrusion detection
Knowledge-based intrusion detection
Statistical anomaly-based intrusion detection
Host-based intrusion detection
There are two conceptual approaches to intrusion detection. Knowledge-based intrusion detection uses a database of known vulnerabilities to look for current attempts to exploit them on a system and trigger an alarm if an attempt is found. The other approach, not as common, is called behaviour-based or statistical analysis-based. A host-based intrusion detection system is a common implementation of intrusion detection, not a conceptual approach.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 63).
Also: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 4: Access Control (pages 193-194).
What IDS approach relies on a database of known attacks?
Signature-based intrusion detection
Statistical anomaly-based intrusion detection
Behavior-based intrusion detection
Network-based intrusion detection
A weakness of the signature-based (or knowledge-based) intrusion detection approach is that only attack signatures that are stored in a database are detected. Network-based intrusion detection can either be signature-based or statistical anomaly-based (also called behavior-based).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 49).
Contracts and agreements are often times unenforceable or hard to enforce in which of the following alternate facility recovery agreement?
hot site
warm site
cold site
reciprocal agreement
A reciprocal agreement is where two or more organizations mutually agree to provide facilities to the other if a disaster occurs. The organizations must have similiar hardware and software configurations. Reciprocal agreements are often not legally binding.
Reciprocal agreements are not contracts and cannot be enforced. You cannot force someone you have such an agreement with to provide processing to you.
Government regulators do not accept reciprocal agreements as valid disaster recovery sites.
Cold sites are empty computer rooms consisting only of environmental systems, such as air conditioning and raised floors, etc. They do not meet the requirements of most regulators and boards of directors that the disaster plan be tested at least annually.
Time Brokers promise to deliver processing time on other systems. They charge a fee, but cannot guaranty that processing will always be available, especially in areas that experienced multiple disasters.
With the exception of providing your own hot site, commercial hot sites provide the greatest protection. Most will allow you up to six weeks to restore your sites if you declare a disaster. They also permit an annual amount of time to test the Disaster Plan.
References:
OIG CBK Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning (pages 368 - 369)
The following answers are incorrect:
hot site. Is incorrect because you have a contract in place stating what services are to be provided.
warm site. Is incorrect because you have a contract in place stating what services are to be provided.
cold site. Is incorrect because you have a contract in place stating what services are to be provided.
Hierarchical Storage Management (HSM) is commonly employed in:
very large data retrieval systems
very small data retrieval systems
shorter data retrieval systems
most data retrieval systems
Hierarchical Storage Management (HSM) is commonly employed in very large data retrieval systems.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 71.
Which backup method is used if backup time is critical and tape space is at an extreme premium?
Incremental backup method.
Differential backup method.
Full backup method.
Tape backup method.
Full Backup/Archival Backup - Complete/Full backup of every selected file on the system regardless of whether it has been backup recently.. This is the slowest of the backup methods since it backups all the data. It’s however the fastest for restoring data.
Incremental Backup - Any backup in which only the files that have been modified since last full back up are backed up. The archive attribute should be updated while backing up only modified files, which indicates that the file has been backed up. This is the fastest of the backup methods, but the slowest of the restore methods.
Differential Backup - The backup of all data files that have been modified since the last incremental backup or archival/full backup. Uses the archive bit to determine what files have changed since last incremental backup or full backup. The files grows each day until the next full backup is performed clearing the archive attributes. This enables the user to restore all files changed since the last full backup in one pass. This is a more neutral method of backing up data since it’s not faster nor slower than the other two
Easy Way To Remember each of the backup type properties:
Backup Speed Restore Speed
Full 3 1
Differential 2 2
Incremental 1 3
Legend: 1 = Fastest 2 = Faster 3 = Slowest
Source:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 69.
and
http://www.proprofs.com/mwiki/index.php/Full_Backup,_Incremental_%26_Differential_Backup
What can be described as an imaginary line that separates the trusted components of the TCB from those elements that are NOT trusted?
The security kernel
The reference monitor
The security perimeter
The reference perimeter
The security perimeter is the imaginary line that separates the trusted components of the kernel and the Trusted Computing Base (TCB) from those elements that are not trusted. The reference monitor is an abstract machine that mediates all accesses to objects by subjects. The security kernel can be software, firmware or hardware components in a trusted system and is the actual instantiation of the reference monitor. The reference perimeter is not defined and is a distracter.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security Architecture and Models, Area 6 CISSP Open Study Guide, January 2002.
What is defined as the hardware, firmware and software elements of a trusted computing base that implement the reference monitor concept?
The reference monitor
Protection rings
A security kernel
A protection domain
A security kernel is defined as the hardware, firmware and software elements of a trusted computing base that implement the reference monitor concept. A reference monitor is a system component that enforces access controls on an object. A protection domain consists of the execution and memory space assigned to each process. The use of protection rings is a scheme that supports multiple protection domains.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 5: Security Architecture and Models (page 194).
Which of the following is not a component of a Operations Security "triples"?
Asset
Threat
Vulnerability
Risk
The Operations Security domain is concerned with triples - threats, vulnerabilities and assets.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 216.
In an organization, an Information Technology security function should:
Be a function within the information systems function of an organization.
Report directly to a specialized business unit such as legal, corporate security or insurance.
Be lead by a Chief Security Officer and report directly to the CEO.
Be independent but report to the Information Systems function.
In order to offer more independence and get more attention from management, an IT security function should be independent from IT and report directly to the CEO. Having it report to a specialized business unit (e.g. legal) is not recommended as it promotes a low technology view of the function and leads people to believe that it is someone else's problem.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security management Practices CISSP Open Study Guide, version 1.0, april 1999.
When backing up an applications system's data, which of the following is a key question to be answered first?
When to make backups
Where to keep backups
What records to backup
How to store backups
It is critical that a determination be made of WHAT data is important and should be retained and protected. Without determining the data to be backed up, the potential for error increases. A record or file could be vital and yet not included in a backup routine. Alternatively, temporary or insignificant files could be included in a backup routine unnecessarily.
The following answers were incorrect:
When to make backups Although it is important to consider schedules for backups, this is done after the decisions are made of what should be included in the backup routine.
Where to keep backups The location of storing backup copies of data (Such as tapes, on-line backups, etc) should be made after determining what should be included in the backup routine and the method to store the backup.
How to store backups The backup methodology should be considered after determining what data should be included in the backup routine.
Related to information security, integrity is the opposite of which of the following?
abstraction
alteration
accreditation
application
Integrity is the opposite of "alteration."
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 59.
Which of the following would provide the BEST stress testing environment taking under consideration and avoiding possible data exposure and leaks of sensitive data?
Test environment using test data.
Test environment using sanitized live workloads data.
Production environment using test data.
Production environment using sanitized live workloads data.
The best way to properly verify an application or system during a stress test would be to expose it to "live" data that has been sanitized to avoid exposing any sensitive information or Personally Identifiable Data (PII) while in a testing environment. Fabricated test data may not be as varied, complex or computationally demanding as "live" data. A production environment should never be used to test a product, as a production environment is one where the application or system is being put to commercial or operational use. It is a best practice to perform testing in a non-production environment.
Stress testing is carried out to ensure a system can cope with production workloads, but as it may be tested to destruction, a test environment should always be used to avoid damaging the production environment. Hence, testing should never take place in a production environment. If only test data is used, there is no certainty that the system was adequately stress tested.
Which of the following should be emphasized during the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) considering that the BIA focus is on business processes?
Composition
Priorities
Dependencies
Service levels
The Business Impact Analysis (BIA) identifies time-critical aspects of the critical business processes, and determines their maximum tolerable downtime. The BIA helps to Identify organization functions, the capabilities of each organization unit to handle outages, and the priority and sequence of functions and applications to be recovered, identify resources required for recovery of those areas and interdependencies
In performing the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) it is very important to consider what the dependencies are. You cannot bring a system up if it depends on another system to be operational. You need to look at not only internal dependencies but external as well. You might not be able to get the raw materials for your business so dependencies are very important aspect of a BIA.
The BIA committee will not truly understand all business processes, the steps that must take place, or the resources and supplies these processes require. So the committee must gather this information from the people who do know— department managers and specific employees throughout the organization. The committee starts by identifying the people who will be part of the BIA data-gathering sessions. The committee needs to identify how it will collect the data from the selected employees, be it through surveys, interviews, or workshops. Next, the team needs to collect the information by actually conducting surveys, interviews, and workshops. Data points obtained as part of the information gathering will be used later during analysis. It is important that the team members ask about how different tasks— whether processes, transactions, or services, along with any relevant dependencies— get accomplished within the organization.
The following answers are incorrect:
composition This is incorrect because it is not the best answer. While the make up of business may be important, if you have not determined the dependencies first you may not be able to bring the critical business processes to a ready state or have the materials on hand that are needed.
priorities This is incorrect because it is not the best answer. While the priorities of processes are important, if you have not determined the dependencies first you may not be able to bring the critical business processes to a ready state or have the materials on hand that are needed.
service levels This is incorrect because it is not the best answer. Service levels are not as important as dependencies.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Schneiter, Andrew (2013-04-15). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition : Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning (Kindle Locations 188-191). . Kindle Edition.
and
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (Kindle Locations 18562-18568). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
What would be considered the biggest drawback of Host-based Intrusion Detection systems (HIDS)?
It can be very invasive to the host operating system
Monitors all processes and activities on the host system only
Virtually eliminates limits associated with encryption
They have an increased level of visibility and control compared to NIDS
The biggest drawback of HIDS, and the reason many organizations resist its use, is that it can be very invasive to the host operating system. HIDS must have the capability to monitor all processes and activities on the host system and this can sometimes interfere with normal system processing.
HIDS versus NIDS
A host-based IDS (HIDS) can be installed on individual workstations and/ or servers to watch for inappropriate or anomalous activity. HIDSs are usually used to make sure users do not delete system files, reconfigure important settings, or put the system at risk in any other way.
So, whereas the NIDS understands and monitors the network traffic, a HIDS’s universe is limited to the computer itself. A HIDS does not understand or review network traffic, and a NIDS does not “look in” and monitor a system’s activity. Each has its own job and stays out of the other’s way.
The ISC2 official study book defines an IDS as:
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a technology that alerts organizations to adverse or unwanted activity. An IDS can be implemented as part of a network device, such as a router, switch, or firewall, or it can be a dedicated IDS device monitoring traffic as it traverses the network. When used in this way, it is referred to as a network IDS, or NIDS. IDS can also be used on individual host systems to monitor and report on file, disk, and process activity on that host. When used in this way it is referred to as a host-based IDS, or HIDS.
An IDS is informative by nature and provides real-time information when suspicious activities are identified. It is primarily a detective device and, acting in this traditional role, is not used to directly prevent the suspected attack.
What about IPS?
In contrast, an intrusion prevention system (IPS), is a technology that monitors activity like an IDS but will automatically take proactive preventative action if it detects unacceptable activity. An IPS permits a predetermined set of functions and actions to occur on a network or system; anything that is not permitted is considered unwanted activity and blocked. IPS is engineered specifically to respond in real time to an event at the system or network layer. By proactively enforcing policy, IPS can thwart not only attackers, but also authorized users attempting to perform an action that is not within policy. Fundamentally, IPS is considered an access control and policy enforcement technology, whereas IDS is considered network monitoring and audit technology.
The following answers were incorrect:
All of the other answer were advantages and not drawback of using HIDS
TIP FOR THE EXAM:
Be familiar with the differences that exists between an HIDS, NIDS, and IPS. Know that IDS's are mostly detective but IPS are preventive. IPS's are considered an access control and policy enforcement technology, whereas IDS's are considered network monitoring and audit technology.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (Kindle Locations 5817-5822). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
and
Schneiter, Andrew (2013-04-15). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition : Access Control ((ISC)2 Press), Domain1, Page 180-188 or on the kindle version look for Kindle Locations 3199-3203. Auerbach Publications.
Which of the following is a disadvantage of a statistical anomaly-based intrusion detection system?
it may truly detect a non-attack event that had caused a momentary anomaly in the system.
it may falsely detect a non-attack event that had caused a momentary anomaly in the system.
it may correctly detect a non-attack event that had caused a momentary anomaly in the system.
it may loosely detect a non-attack event that had caused a momentary anomaly in the system.
Some disadvantages of a statistical anomaly-based ID are that it will not detect an attack that does not significantly change the system operating characteristics, or it may falsely detect a non-attack event that had caused a momentary anomaly in the system.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 49.
Which of the following algorithms is a stream cipher?
RC2
RC4
RC5
RC6
RC2, RC4, RC5 and RC6 were developed by Ronal Rivest from RSA Security.
In the RC family only RC4 is a stream cipher.
RC4 allows a variable key length.
RC2 works with 64-bit blocks and variable key lengths,
RC5 has variable block sizes, key length and number of processing rounds.
RC6 was designed to fix a flaw in RC5.
Source: ANDRESS, Mandy, Exam Cram CISSP, Coriolis, 2001, Chapter 6: Cryptography (page 103).
What can be defined as a momentary low voltage?
Spike
Sag
Fault
Brownout
A sag is a momentary low voltage. A spike is a momentary high voltage. A fault is a momentary power out and a brownout is a prolonged power supply that is below normal voltage.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 6: Physical security (page 299)
The absence of a safeguard, or a weakness in a system that may possibly be exploited is called a(n)?
Threat
Exposure
Vulnerability
Risk
A vulnerability is a weakness in a system that can be exploited by a threat.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 237.
A deviation from an organization-wide security policy requires which of the following?
Risk Acceptance
Risk Assignment
Risk Reduction
Risk Containment
A deviation from an organization-wide security policy requires you to manage the risk. If you deviate from the security policy then you are required to accept the risks that might occur.
In some cases, it may be prudent for an organization to simply accept the risk that is presented in certain scenarios. Risk acceptance is the practice of accepting certain risk(s), typically based on a business decision that may also weigh the cost versus the benefit of dealing with the risk in another way.
The OIG defines Risk Management as: This term characterizes the overall process.
The first phase of risk assessment includes identifying risks, risk-reducing measures, and the budgetary impact of implementing decisions related to the acceptance, avoidance, or transfer of risk.
The second phase of risk management includes the process of assigning priority to, budgeting, implementing, and maintaining appropriate risk-reducing measures.
Risk management is a continuous process of ever-increasing complexity. It is how we evaluate the impact of exposures and respond to them. Risk management minimizes loss to information assets due to undesirable events through identification, measurement, and control. It encompasses the overall security review, risk analysis, selection and evaluation of safeguards, cost–benefit analysis, management decision, and safeguard identification and implementation, along with ongoing effectiveness review.
Risk management provides a mechanism to the organization to ensure that executive management knows current risks, and informed decisions can be made to use one of the risk management principles: risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk mitigation, or risk acceptance.
The 4 ways of dealing with risks are: Avoidance, Transfer, Mitigation, Acceptance
The following answers are incorrect:
Risk assignment. Is incorrect because it is a distractor, assignment is not one of the ways to manage risk.
Risk reduction. Is incorrect because there was a deviation of the security policy. You could have some additional exposure by the fact that you deviated from the policy.
Risk containment. Is incorrect because it is a distractor, containment is not one of the ways to manage risk.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 8882-8886). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 10206-10208). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
The IP header contains a protocol field. If this field contains the value of 51, what type of data is contained within the ip datagram?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Authentication Header (AH)
User datagram protocol (UDP)
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
TCP has the value of 6
UDP has the value of 17
ICMP has the value of 1
Compared to RSA, which of the following is true of Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC)?
It has been mathematically proved to be more secure.
It has been mathematically proved to be less secure.
It is believed to require longer key for equivalent security.
It is believed to require shorter keys for equivalent security.
The following answers are incorrect: It has been mathematically proved to be less secure. ECC has not been proved to be more or less secure than RSA. Since ECC is newer than RSA, it is considered riskier by some, but that is just a general assessment, not based on mathematical arguments.
It has been mathematically proved to be more secure. ECC has not been proved to be more or less secure than RSA. Since ECC is newer than RSA, it is considered riskier by some, but that is just a general assessment, not based on mathematical arguments.
It is believed to require longer key for equivalent security. On the contrary, it is believed to require shorter keys for equivalent security of RSA.
Shon Harris, AIO v5 pg719 states:
"In most cases, the longer the key, the more protection that is provided, but ECC can provide the same level of protection with a key size that is shorter that what RSA requires"
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
ISC2 OIG, 2007 p. 258
Shon Harris, AIO v5 pg719
Which of the following is best at defeating frequency analysis?
Substitution cipher
Polyalphabetic cipher
Transposition cipher
Ceasar Cipher
Simple substitution and transposition ciphers are vulnerable to attacks that perform frequency analysis.
In every language, there are words and patterns that are used more than others.
Some patterns common to a language can actually help attackers figure out the transformation between plaintext and ciphertext, which enables them to figure out the key that was used to perform the transformation. Polyalphabetic ciphers use different alphabets to defeat frequency analysis.
The ceasar cipher is a very simple substitution cipher that can be easily defeated and it does show repeating letters.
Out of list presented, it is the Polyalphabetic cipher that would provide the best protection against simple frequency analysis attacks.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 8: Cryptography (page 507).
And : DUPUIS, Clement, CISSP Open Study Guide on domain 5, cryptography, April 1999.
What is the role of IKE within the IPsec protocol?
peer authentication and key exchange
data encryption
data signature
enforcing quality of service
Which of the following offers confidentiality to an e-mail message?
The sender encrypting it with its private key.
The sender encrypting it with its public key.
The sender encrypting it with the receiver's public key.
The sender encrypting it with the receiver's private key.
An e-mail message's confidentiality is protected when encrypted with the receiver's public key, because he is the only one able to decrypt the message. The sender is not supposed to have the receiver's private key. By encrypting a message with its private key, anybody possessing the corresponding public key would be able to read the message. By encrypting the message with its public key, not even the receiver would be able to read the message.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 517).
Which of the following virus types changes some of its characteristics as it spreads?
Boot Sector
Parasitic
Stealth
Polymorphic
A Polymorphic virus produces varied but operational copies of itself in hopes of evading anti-virus software.
The following answers are incorrect:
boot sector. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A boot sector virus attacks the boot sector of a drive. It describes the type of attack of the virus and not the characteristics of its composition.
parasitic. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A parasitic virus attaches itself to other files but does not change its characteristics.
stealth. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A stealth virus attempts to hide changes of the affected files but not itself.
Which of the following security mode of operation does NOT require all users to have the clearance for all information processed on the system?
Compartmented security mode
Multilevel security mode
System-high security mode
Dedicated security mode
The multilevel security mode permits two or more classification levels of information to be processed at the same time when all the users do not have the clearance of formal approval to access all the information being processed by the system.
In dedicated security mode, all users have the clearance or authorization and need-to-know to all data processed within the system.
In system-high security mode, all users have a security clearance or authorization to access the information but not necessarily a need-to-know for all the information processed on the system (only some of the data).
In compartmented security mode, all users have the clearance to access all the information processed by the system, but might not have the need-to-know and formal access approval.
Generally, Security modes refer to information systems security modes of operations used in mandatory access control (MAC) systems. Often, these systems contain information at various levels of security classification.
The mode of operation is determined by:
The type of users who will be directly or indirectly accessing the system.
The type of data, including classification levels, compartments, and categories, that are processed on the system.
The type of levels of users, their need to know, and formal access approvals that the users will have.
Dedicated security mode
In this mode of operation, all users must have:
Signed NDA for ALL information on the system.
Proper clearance for ALL information on the system.
Formal access approval for ALL information on the system.
A valid need to know for ALL information on the system.
All users can access ALL data.
System high security mode
In this mode of operation, all users must have:
Signed NDA for ALL information on the system.
Proper clearance for ALL information on the system.
Formal access approval for ALL information on the system.
A valid need to know for SOME information on the system.
All users can access SOME data, based on their need to know.
Compartmented security mode
In this mode of operation, all users must have:
Signed NDA for ALL information on the system.
Proper clearance for ALL information on the system.
Formal access approval for SOME information they will access on the system.
A valid need to know for SOME information on the system.
All users can access SOME data, based on their need to know and formal access approval.
Multilevel security mode
In this mode of operation, all users must have:
Signed NDA for ALL information on the system.
Proper clearance for SOME information on the system.
Formal access approval for SOME information on the system.
A valid need to know for SOME information on the system.
All users can access SOME data, based on their need to know, clearance and formal access approval.
REFERENCES:
WALLHOFF, John, CBK#6 Security Architecture and Models (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 6).
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Security_Modes
Which of the following Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) uses a database of attacks, known system vulnerabilities, monitoring current attempts to exploit those vulnerabilities, and then triggers an alarm if an attempt is found?
Knowledge-Based ID System
Application-Based ID System
Host-Based ID System
Network-Based ID System
Knowledge-based Intrusion Detection Systems use a database of previous attacks and known system vulnerabilities to look for current attempts to exploit their vulnerabilities, and trigger an alarm if an attempt is found.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 87.
Application-Based ID System - "a subset of HIDS that analyze what's going on in an application using the transaction log files of the application." Source: Official ISC2 CISSP CBK Review Seminar Student Manual Version 7.0 p. 87
Host-Based ID System - "an implementation of IDS capabilities at the host level. Its most significant difference from NIDS is intrusion detection analysis, and related processes are limited to the boundaries of the host." Source: Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK - p. 197
Network-Based ID System - "a network device, or dedicated system attached to teh network, that monitors traffic traversing teh network segment for which it is integrated." Source: Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK - p. 196
Which of the following statements pertaining to link encryption is false?
It encrypts all the data along a specific communication path.
It provides protection against packet sniffers and eavesdroppers.
Information stays encrypted from one end of its journey to the other.
User information, header, trailers, addresses and routing data that are part of the packets are encrypted.
When using link encryption, packets have to be decrypted at each hop and encrypted again.
Information staying encrypted from one end of its journey to the other is a characteristic of end-to-end encryption, not link encryption.
Link Encryption vs. End-to-End Encryption
Link encryption encrypts the entire packet, including headers and trailers, and has to be decrypted at each hop.
End-to-end encryption does not encrypt the IP Protocol headers, and therefore does not need to be decrypted at each hop.
What is a packet sniffer?
It tracks network connections to off-site locations.
It monitors network traffic for illegal packets.
It scans network segments for cabling faults.
It captures network traffic for later analysis.
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
In stateful inspection firewalls, packets are:
Inspected at only one layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model
Inspected at all Open System Interconnection (OSI) layers
Decapsulated at all Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) layers.
Encapsulated at all Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) layers.
Many times when a connection is opened, the firewall will inspect all layers of the packet. While this inspection is scaled back for subsequent packets to improve performance, this is the best of the four answers.
When packet filtering is used, a packet arrives at the firewall, and it runs through its ACLs to determine whether this packet should be allowed or denied. If the packet is allowed, it is passed on to the destination host, or to another network device, and the packet filtering device forgets about the packet. This is different from stateful inspection, which remembers and keeps track of what packets went where until each particular connection is closed. A stateful firewall is like a nosy neighbor who gets into people’s business and conversations. She keeps track of the suspicious cars that come into the neighborhood, who is out of town for the week, and the postman who stays a little too long at the neighbor lady’s house. This can be annoying until your house is burglarized. Then you and the police will want to talk to the nosy neighbor, because she knows everything going on in the neighborhood and would be the one most likely to know something unusual happened.
"Inspected at only one Open Systems Interconnetion (OSI) layer" is incorrect. To perform stateful packet inspection, the firewall must consider at least the network and transport layers.
"Decapsulated at all Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) layers" is incorrect. The headers are not stripped ("decapsulated" if there is such a word) and are passed through in their entirety IF the packet is passed.
"Encapsulated at all Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) layers" is incorrect. Encapsulation refers to the adding of a layer's header/trailer to the information received from the above level. This is done when the packet is assembled not at the firewall.
Reference(s) used for this question:
CBK, p. 466
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (pp. 632-633). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
Layer 4 of the OSI stack is known as:
the data link layer
the transport layer
the network layer
the presentation layer
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
What type of attack involves IP spoofing, ICMP ECHO and a bounce site?
IP spoofing attack
Teardrop attack
SYN attack
Smurf attack
A smurf attack occurs when an attacker sends a spoofed (IP spoofing) PING (ICMP ECHO) packet to the broadcast address of a large network (the bounce site). The modified packet containing the address of the target system, all devices on its local network respond with a ICMP REPLY to the target system, which is then saturated with those replies. An IP spoofing attack is used to convince a system that it is communication with a known entity that gives an intruder access. It involves modifying the source address of a packet for a trusted source's address. A teardrop attack consists of modifying the length and fragmentation offset fields in sequential IP packets so the target system becomes confused and crashes after it receives contradictory instructions on how the fragments are offset on these packets. A SYN attack is when an attacker floods a system with connection requests but does not respond when the target system replies to those requests.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 76).
What is the greatest danger from DHCP?
An intruder on the network impersonating a DHCP server and thereby misconfiguring the DHCP clients.
Having multiple clients on the same LAN having the same IP address.
Having the wrong router used as the default gateway.
Having the organization's mail server unreachable.
The greatest danger from BootP or DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) is from an intruder on the network impersonating a DHCP server and thereby misconfiguring the DHCP clients. Other choices are possible consequences of DHCP impersonation.
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 4: Sockets and Services from a Security Viewpoint.
Which one of the following statements about the advantages and disadvantages of network-based Intrusion detection systems is true
Network-based IDSs are not vulnerable to attacks.
Network-based IDSs are well suited for modern switch-based networks.
Most network-based IDSs can automatically indicate whether or not an attack was successful.
The deployment of network-based IDSs has little impact upon an existing network.
Network-based IDSs are usually passive devices that listen on a network wire without interfering with the normal operation of a network. Thus, it is usually easy to retrofit a network to include network-based IDSs with minimal effort.
Network-based IDSs are not vulnerable to attacks is not true, even thou network-based IDSs can be made very secure against attack and even made invisible to many attackers they still have to read the packets and sometimes a well crafted packet might exploit or kill your capture engine.
Network-based IDSs are well suited for modern switch-based networks is not true as most switches do not provide universal monitoring ports and this limits the monitoring range of a network-based IDS sensor to a single host. Even when switches provide such monitoring ports, often the single port cannot mirror all traffic traversing the switch.
Most network-based IDSs can automatically indicate whether or not an attack was successful is not true as most network-based IDSs cannot tell whether or not an attack was successful; they can only discern that an attack was initiated. This means that after a network-based IDS detects an attack, administrators must manually investigate each attacked host to determine whether it was indeed penetrated.
The Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC) was written to address which of the following that the Orange Book did not address?
integrity and confidentiality.
confidentiality and availability.
integrity and availability.
none of the above.
TCSEC focused on confidentiality while ITSEC added integrity and availability as security goals.
The following answers are incorrect:
integrity and confidentiality. Is incorrect because TCSEC addressed confidentiality.
confidentiality and availability. Is incorrect because TCSEC addressed confidentiality.
none of the above. Is incorrect because ITSEC added integrity and availability as security goals.
Which property ensures that only the intended recipient can access the data and nobody else?
Confidentiality
Capability
Integrity
Availability
Confidentiality is defined as the property that ensures that only the intended recipient can access the data and nobody else. It is usually achieve using cryptogrphic methods, tools, and protocols.
Confidentiality supports the principle of “least privilege” by providing that only authorized individuals, processes, or systems should have access to information on a need-to-know basis. The level of access that an authorized individual should have is at the level necessary for them to do their job. In recent years, much press has been dedicated to the privacy of information and the need to protect it from individuals, who may be able to commit crimes by viewing the information. Identity theft is the act of assuming one’s identity through knowledge of confidential information obtained from various sources.
The following are incorrect answers:
Capability is incorrect. Capability is relevant to access control. Capability-based security is a concept in the design of secure computing systems, one of the existing security models. A capability (known in some systems as a key) is a communicable, unforgeable token of authority. It refers to a value that references an object along with an associated set of access rights. A user program on a capability-based operating system must use a capability to access an object. Capability-based security refers to the principle of designing user programs such that they directly share capabilities with each other according to the principle of least privilege, and to the operating system infrastructure necessary to make such transactions efficient and secure.
Integrity is incorrect. Integrity protects information from unauthorized modification or loss.
Availability is incorrect. Availability assures that information and services are available for use by authorized entities according to the service level objective.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 9345-9349). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capability-based_security
What is malware that can spread itself over open network connections?
Worm
Rootkit
Adware
Logic Bomb
Computer worms are also known as Network Mobile Code, or a virus-like bit of code that can replicate itself over a network, infecting adjacent computers.
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer.
A notable example is the SQL Slammer computer worm that spread globally in ten minutes on January 25, 2003. I myself came to work that day as a software tester and found all my SQL servers infected and actively trying to infect other computers on the test network.
A patch had been released a year prior by Microsoft and if systems were not patched and exposed to a 376 byte UDP packet from an infected host then system would become compromised.
Ordinarily, infected computers are not to be trusted and must be rebuilt from scratch but the vulnerability could be mitigated by replacing a single vulnerable dll called sqlsort.dll.
Replacing that with the patched version completely disabled the worm which really illustrates to us the importance of actively patching our systems against such network mobile code.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Rootkit: Sorry, this isn't correct because a rootkit isn't ordinarily classified as network mobile code like a worm is. This isn't to say that a rootkit couldn't be included in a worm, just that a rootkit isn't usually classified like a worm. A rootkit is a stealthy type of software, typically malicious, designed to hide the existence of certain processes or programs from normal methods of detection and enable continued privileged access to a computer. The term rootkit is a concatenation of "root" (the traditional name of the privileged account on Unix operating systems) and the word "kit" (which refers to the software components that implement the tool). The term "rootkit" has negative connotations through its association with malware.
- Adware: Incorrect answer. Sorry but adware isn't usually classified as a worm. Adware, or advertising-supported software, is any software package which automatically renders advertisements in order to generate revenue for its author. The advertisements may be in the user interface of the software or on a screen presented to the user during the installation process. The functions may be designed to analyze which Internet sites the user visits and to present advertising pertinent to the types of goods or services featured there. The term is sometimes used to refer to software that displays unwanted advertisements.
- Logic Bomb: Logic bombs like adware or rootkits could be spread by worms if they exploit the right service and gain root or admin access on a computer.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
The CCCure CompTIA Holistic Security+ Tutorial and CBT
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rootkit
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_worm
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adware
Virus scanning and content inspection of SMIME encrypted e-mail without doing any further processing is:
Not possible
Only possible with key recovery scheme of all user keys
It is possible only if X509 Version 3 certificates are used
It is possible only by "brute force" decryption
Content security measures presumes that the content is available in cleartext on the central mail server.
Encrypted emails have to be decrypted before it can be filtered (e.g. to detect viruses), so you need the decryption key on the central "crypto mail server".
There are several ways for such key management, e.g. by message or key recovery methods. However, that would certainly require further processing in order to achieve such goal.
The high availability of multiple all-inclusive, easy-to-use hacking tools that do NOT require much technical knowledge has brought a growth in the number of which type of attackers?
Black hats
White hats
Script kiddies
Phreakers
As script kiddies are low to moderately skilled hackers using available scripts and tools to easily launch attacks against victims.
The other answers are incorrect because :
Black hats is incorrect as they are malicious , skilled hackers.
White hats is incorrect as they are security professionals.
Phreakers is incorrect as they are telephone/PBX (private branch exchange) hackers.
Reference : Shon Harris AIO v3 , Chapter 12: Operations security , Page : 830
What do the ILOVEYOU and Melissa virus attacks have in common?
They are both denial-of-service (DOS) attacks.
They have nothing in common.
They are both masquerading attacks.
They are both social engineering attacks.
While a masquerading attack can be considered a type of social engineering, the Melissa and ILOVEYOU viruses are examples of masquerading attacks, even if it may cause some kind of denial of service due to the web server being flooded with messages. In this case, the receiver confidently opens a message coming from a trusted individual, only to find that the message was sent using the trusted party's identity.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 10: Law, Investigation, and Ethics (page 650).
What best describes a scenario when an employee has been shaving off pennies from multiple accounts and depositing the funds into his own bank account?
Data fiddling
Data diddling
Salami techniques
Trojan horses
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2001, Page 644.
Crackers today are MOST often motivated by their desire to:
Help the community in securing their networks.
Seeing how far their skills will take them.
Getting recognition for their actions.
Gaining Money or Financial Gains.
A few years ago the best choice for this question would have been seeing how far their skills can take them. Today this has changed greatly, most crimes committed are financially motivated.
Profit is the most widespread motive behind all cybercrimes and, indeed, most crimes- everyone wants to make money. Hacking for money or for free services includes a smorgasbord of crimes such as embezzlement, corporate espionage and being a “hacker for hire”. Scams are easier to undertake but the likelihood of success is much lower. Money-seekers come from any lifestyle but those with persuasive skills make better con artists in the same way as those who are exceptionally tech-savvy make better “hacks for hire”.
"White hats" are the security specialists (as opposed to Black Hats) interested in helping the community in securing their networks. They will test systems and network with the owner authorization.
A Black Hat is someone who uses his skills for offensive purpose. They do not seek authorization before they attempt to comprise the security mechanisms in place.
"Grey Hats" are people who sometimes work as a White hat and other times they will work as a "Black Hat", they have not made up their mind yet as to which side they prefer to be.
The following are incorrect answers:
All the other choices could be possible reasons but the best one today is really for financial gains.
References used for this question:
http://library.thinkquest.org/04oct/00460/crimeMotives.html
and
http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1160835
and
http://www.aic.gov.au/documents/1/B/A/%7B1BA0F612-613A-494D-B6C5-06938FE8BB53%7Dhtcb006.pdf
Which of the following computer crime is MORE often associated with INSIDERS?
IP spoofing
Password sniffing
Data diddling
Denial of service (DOS)
It refers to the alteration of the existing data , most often seen before it is entered into an application.This type of crime is extremely common and can be prevented by using appropriate access controls and proper segregation of duties. It will more likely be perpetrated by insiders, who have access to data before it is processed.
The other answers are incorrect because :
IP Spoofing is not correct as the questions asks about the crime associated with the insiders. Spoofing is generally accomplished from the outside.
Password sniffing is also not the BEST answer as it requires a lot of technical knowledge in understanding the encryption and decryption process.
Denial of service (DOS) is also incorrect as most Denial of service attacks occur over the internet.
Reference : Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter-10 : Law , Investigation & Ethics , Page : 758-760.
Which virus category has the capability of changing its own code, making it harder to detect by anti-virus software?
Stealth viruses
Polymorphic viruses
Trojan horses
Logic bombs
A polymorphic virus has the capability of changing its own code, enabling it to have many different variants, making it harder to detect by anti-virus software. The particularity of a stealth virus is that it tries to hide its presence after infecting a system. A Trojan horse is a set of unauthorized instructions that are added to or replacing a legitimate program. A logic bomb is a set of instructions that is initiated when a specific event occurs.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 786).
Which of the following technologies is a target of XSS or CSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attacks?
Web Applications
Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls
DNS Servers
XSS or Cross-Site Scripting is a threat to web applications where malicious code is placed on a website that attacks the use using their existing authenticated session status.
Cross-Site Scripting attacks are a type of injection problem, in which malicious scripts are injected into the otherwise benign and trusted web sites. Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks occur when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user. Flaws that allow these attacks to succeed are quite widespread and occur anywhere a web application uses input from a user in the output it generates without validating or encoding it.
An attacker can use XSS to send a malicious script to an unsuspecting user. The end user’s browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script. Because it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by your browser and used with that site. These scripts can even rewrite the content of the HTML page.
Mitigation:
Configure your IPS - Intrusion Prevention System to detect and suppress this traffic.
Input Validation on the web application to normalize inputted data.
Set web apps to bind session cookies to the IP Address of the legitimate user and only permit that IP Address to use that cookie.
See the XSS (Cross Site Scripting) Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the Abridged XSS Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the DOM based XSS Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the OWASP Development Guide article on Phishing.
See the OWASP Development Guide article on Data Validation.
The following answers are incorrect:
Intrusion Detection Systems: Sorry. IDS Systems aren't usually the target of XSS attacks but a properly-configured IDS/IPS can "detect and report on malicious string and suppress the TCP connection in an attempt to mitigate the threat.
Firewalls: Sorry. Firewalls aren't usually the target of XSS attacks.
DNS Servers: Same as above, DNS Servers aren't usually targeted in XSS attacks but they play a key role in the domain name resolution in the XSS attack process.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
CCCure Holistic Security+ CBT and Curriculum
and
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Cross-site_Scripting_%28XSS%29
A DMZ is located:
right behind your first Internet facing firewall
right in front of your first Internet facing firewall
right behind your first network active firewall
right behind your first network passive Internet http firewall
While the purpose of systems in the DMZ is to allow public access to certain internal network resources (EMAIL, DNS, Web), it is a good practice to restrict that access to the minimum necessary to provide those services through use of a firewall.
In computer security, a DMZ or Demilitarized Zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization's external-facing services to a larger and untrusted network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization's local area network (LAN); an external attacker only has direct access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network. The name is derived from the term "demilitarized zone", an area between nation states in which military operation is not permitted.
The following are incorrect answers:
"Right in front of your first Internet facing firewall" While the purpose of systems in the DMZ is to allow public access to certain internal network resources (EMAIL, DNS, Web), it is a good practice to restrict that access to the minimum necessary to provide those services through use of a firewall.
"Right behind your first network active firewall" This is an almost-right-sounding answer meant to distract the unwary.
"Right behind your first network passive Internet http firewall" This is an almost-right-sounding answer meant to distract the unwary.
References:
CBK, p. 434
and
AIO3, p. 483
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DMZ_%28computing%29
Which of the following questions are least likely to help in assessing controls covering audit trails?
Does the audit trail provide a trace of user actions?
Are incidents monitored and tracked until resolved?
Is access to online logs strictly controlled?
Is there separation of duties between security personnel who administer the access control function and those who administer the audit trail?
Audit trails maintain a record of system activity by system or application processes and by user activity. In conjunction with appropriate tools and procedures, audit trails can provide individual accountability, a means to reconstruct events, detect intrusions, and identify problems. Audit trail controls are considered technical controls. Monitoring and tracking of incidents is more an operational control related to incident response capability.
Reference(s) used for this question:
SWANSON, Marianne, NIST Special Publication 800-26, Security Self-Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems, November 2001 (Pages A-50 to A-51).
NOTE: NIST SP 800-26 has been superceded By: FIPS 200, SP 800-53, SP 800-53A
You can find the new replacement at: http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/PubsSPs.html
However, if you really wish to see the old standard, it is listed as an archived document at:
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/PubsSPArch.html
A prolonged complete loss of electric power is a:
brownout
blackout
surge
fault
A prolonged power outage is a blackout.
From: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 3rd. Edition McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2005, page 368.
Which one of the following is NOT one of the outcomes of a vulnerability assessment?
Quantative loss assessment
Qualitative loss assessment
Formal approval of BCP scope and initiation document
Defining critical support areas
When seeking to determine the security position of an organization, the security professional will eventually turn to a vulnerability assessment to help identify specific areas of weakness that need to be addressed. A vulnerability assessment is the use of various tools and analysis methodologies to determine where a particular system or process may be susceptible to attack or misuse. Most vulnerability assessments concentrate on technical vulnerabilities in systems or applications, but the assessment process is equally as effective when examining physical or administrative business processes.
The vulnerability assessment is often part of a BIA. It is similar to a Risk Assessment in that there is a quantitative (financial) section and a qualitative (operational) section. It differs in that i t is smaller than a full risk assessment and is focused on providing information that is used solely for the business continuity plan or disaster recovery plan.
A function of a vulnerability assessment is to conduct a loss impact analysis. Because there will be two parts to the assessment, a financial assessment and an operational assessment, it will be necessary to define loss criteria both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Quantitative loss criteria may be defined as follows:
Incurring financial losses from loss of revenue, capital expenditure, or personal liability resolution
The additional operational expenses incurred due to the disruptive event
Incurring financial loss from resolution of violation of contract agreements
Incurring financial loss from resolution of violation of regulatory or compliance requirements
Qualitative loss criteria may consist of the following:
The loss of competitive advantage or market share
The loss of public confidence or credibility, or incurring public mbarrassment
During the vulnerability assessment, critical support areas must be defined in order to assess the impact of a disruptive event. A critical support area is defined as a business unit or function that must be present to sustain continuity of the business processes, maintain life safety, or avoid public relations embarrassment.
Critical support areas could include the following:
Telecommunications, data communications, or information technology areas
Physical infrastructure or plant facilities, transportation services
Accounting, payroll, transaction processing, customer service, purchasing
The granular elements of these critical support areas will also need to be identified. By granular elements we mean the personnel, resources, and services the critical support areas need to maintain business continuity
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 4628-4632). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Page 277.
Which of the following best describes what would be expected at a "hot site"?
Computers, climate control, cables and peripherals
Computers and peripherals
Computers and dedicated climate control systems.
Dedicated climate control systems
A Hot Site contains everything needed to become operational in the shortest amount of time.
The following answers are incorrect:
Computers and peripherals. Is incorrect because no mention is made of cables. You would not be fully operational without those.
Computers and dedicated climate control systems. Is incorrect because no mention is made of peripherals. You would not be fully operational without those.
Dedicated climate control systems. Is incorrect because no mentionis made of computers, cables and peripherals. You would not be fully operational without those.
According to the OIG, a hot site is defined as a fully configured site with complete customer required hardware and software provided by the service provider. A hot site in the context of the CBK is always a RENTAL place. If you have your own site fully equipped that you make use of in case of disaster that would be called a redundant site or an alternate site.
Wikipedia: "A hot site is a duplicate of the original site of the organization, with full computer systems as well as near-complete backups of user data."
References:
OIG CBK, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning (pages 367 - 368)
AIO, 3rd Edition, Business Continuity Planning (pages 709 - 714)
AIO, 4th Edition, Business Continuity Planning , p 790.
Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot_site#Hot_Sites
What is the essential difference between a self-audit and an independent audit?
Tools used
Results
Objectivity
Competence
To maintain operational assurance, organizations use two basic methods: system audits and monitoring. Monitoring refers to an ongoing activity whereas audits are one-time or periodic events and can be either internal or external. The essential difference between a self-audit and an independent audit is objectivity, thus indirectly affecting the results of the audit. Internal and external auditors should have the same level of competence and can use the same tools.
Source: SWANSON, Marianne & GUTTMAN, Barbara, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST Special Publication 800-14, Generally Accepted Principles and Practices for Securing Information Technology Systems, September 1996 (page 25).
Attributes that characterize an attack are stored for reference using which of the following Intrusion Detection System (IDS) ?
signature-based IDS
statistical anomaly-based IDS
event-based IDS
inferent-based IDS
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 49.
Which of the following is an issue with signature-based intrusion detection systems?
Only previously identified attack signatures are detected.
Signature databases must be augmented with inferential elements.
It runs only on the windows operating system
Hackers can circumvent signature evaluations.
An issue with signature-based ID is that only attack signatures that are stored in their database are detected.
New attacks without a signature would not be reported. They do require constant updates in order to maintain their effectiveness.
Reference used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 49.
In an online transaction processing system (OLTP), which of the following actions should be taken when erroneous or invalid transactions are detected?
The transactions should be dropped from processing.
The transactions should be processed after the program makes adjustments.
The transactions should be written to a report and reviewed.
The transactions should be corrected and reprocessed.
In an online transaction processing system (OLTP) all transactions are recorded as they occur. When erroneous or invalid transactions are detected the transaction can be recovered by reviewing the logs.
As explained in the ISC2 OIG:
OLTP is designed to record all of the business transactions of an organization as they occur. It is a data processing system facilitating and managing transaction-oriented applications. These are characterized as a system used by many concurrent users who are actively adding and modifying data to effectively change real-time data.
OLTP environments are frequently found in the finance, telecommunications, insurance, retail, transportation, and travel industries. For example, airline ticket agents enter data in the database in real-time by creating and modifying travel reservations, and these are increasingly joined by users directly making their own reservations and purchasing tickets through airline company Web sites as well as discount travel Web site portals. Therefore, millions of people may be accessing the same flight database every day, and dozens of people may be looking at a specific flight at the same time.
The security concerns for OLTP systems are concurrency and atomicity.
Concurrency controls ensure that two users cannot simultaneously change the same data, or that one user cannot make changes before another user is finished with it. In an airline ticket system, it is critical for an agent processing a reservation to complete the transaction, especially if it is the last seat available on the plane.
Atomicity ensures that all of the steps involved in the transaction complete successfully. If one step should fail, then the other steps should not be able to complete. Again, in an airline ticketing system, if the agent does not enter a name into the name data field correctly, the transaction should not be able to complete.
OLTP systems should act as a monitoring system and detect when individual processes abort, automatically restart an aborted process, back out of a transaction if necessary, allow distribution of multiple copies of application servers across machines, and perform dynamic load balancing.
A security feature uses transaction logs to record information on a transaction before it is processed, and then mark it as processed after it is done. If the system fails during the transaction, the transaction can be recovered by reviewing the transaction logs.
Checkpoint restart is the process of using the transaction logs to restart the machine by running through the log to the last checkpoint or good transaction. All transactions following the last checkpoint are applied before allowing users to access the data again.
Wikipedia has nice coverage on what is OLTP:
Online transaction processing, or OLTP, refers to a class of systems that facilitate and manage transaction-oriented applications, typically for data entry and retrieval transaction processing. The term is somewhat ambiguous; some understand a "transaction" in the context of computer or database transactions, while others (such as the Transaction Processing Performance Council) define it in terms of business or commercial transactions.
OLTP has also been used to refer to processing in which the system responds immediately to user requests. An automatic teller machine (ATM) for a bank is an example of a commercial transaction processing application.
The technology is used in a number of industries, including banking, airlines, mailorder, supermarkets, and manufacturing. Applications include electronic banking, order processing, employee time clock systems, e-commerce, and eTrading.
There are two security concerns for OLTP system: Concurrency and Atomicity
ATOMICITY
In database systems, atomicity (or atomicness) is one of the ACID transaction properties. In an atomic transaction, a series of database operations either all occur, or nothing occurs. A guarantee of atomicity prevents updates to the database occurring only partially, which can cause greater problems than rejecting the whole series outright.
The etymology of the phrase originates in the Classical Greek concept of a fundamental and indivisible component; see atom.
An example of atomicity is ordering an airline ticket where two actions are required: payment, and a seat reservation. The potential passenger must either:
both pay for and reserve a seat; OR
neither pay for nor reserve a seat.
The booking system does not consider it acceptable for a customer to pay for a ticket without securing the seat, nor to reserve the seat without payment succeeding.
CONCURRENCY
Database concurrency controls ensure that transactions occur in an ordered fashion.
The main job of these controls is to protect transactions issued by different users/applications from the effects of each other. They must preserve the four characteristics of database transactions ACID test: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. Read http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ACID for more details on the ACID test.
Thus concurrency control is an essential element for correctness in any system where two database transactions or more, executed with time overlap, can access the same data, e.g., virtually in any general-purpose database system. A well established concurrency control theory exists for database systems: serializability theory, which allows to effectively design and analyze concurrency control methods and mechanisms.
Concurrency is not an issue in itself, it is the lack of proper concurrency controls that makes it a serious issue.
The following answers are incorrect:
The transactions should be dropped from processing. Is incorrect because the transactions are processed and when erroneous or invalid transactions are detected the transaction can be recovered by reviewing the logs.
The transactions should be processed after the program makes adjustments. Is incorrect because the transactions are processed and when erroneous or invalid transactions are detected the transaction can be recovered by reviewing the logs.
The transactions should be corrected and reprocessed. Is incorrect because the transactions are processed and when erroneous or invalid transactions are detected the transaction can be recovered by reviewing the logs.
References:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 12749-12768). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_transaction_processing
and
http://databases.about.com/od/administration/g/concurrency.htm
In the process of gathering evidence from a computer attack, a system administrator took a series of actions which are listed below. Can you identify which one of these actions has compromised the whole evidence collection process?
Using a write blocker
Made a full-disk image
Created a message digest for log files
Displayed the contents of a folder
Displaying the directory contents of a folder can alter the last access time on each listed file.
Using a write blocker is wrong because using a write blocker ensure that you cannot modify the data on the host and it prevent the host from writing to its hard drives.
Made a full-disk image is wrong because making a full-disk image can preserve all data on a hard disk, including deleted files and file fragments.
Created a message digest for log files is wrong because creating a message digest for log files. A message digest is a cryptographic checksum that can demonstrate that the integrity of a file has not been compromised (e.g. changes to the content of a log file)
Domain: LEGAL, REGULATIONS, COMPLIANCE AND INVESTIGATIONS
References:
AIO 3rd Edition, page 783-784
NIST 800-61 Computer Security Incident Handling guide page 3-18 to 3-20
Which of the following tools is less likely to be used by a hacker?
l0phtcrack
Tripwire
OphCrack
John the Ripper
Tripwire is an integrity checking product, triggering alarms when important files (e.g. system or configuration files) are modified.
This is a tool that is not likely to be used by hackers, other than for studying its workings in order to circumvent it.
Other programs are password-cracking programs and are likely to be used by security administrators as well as by hackers. More info regarding Tripwire available on the Tripwire, Inc. Web Site.
NOTE:
The biggest competitor to the commercial version of Tripwire is the freeware version of Tripwire. You can get the Open Source version of Tripwire at the following URL: http://sourceforge.net/projects/tripwire/
The session layer provides a logical persistent connection between peer hosts. Which of the following is one of the modes used in the session layer to establish this connection?
Full duplex
Synchronous
Asynchronous
Half simplex
Layer 5 of the OSI model is the Session Layer. This layer provides a logical persistent connection between peer hosts. A session is analogous to a conversation that is necessary for applications to exchange information.
The session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and closing end-to-end connections, called sessions, between applications located at different network endpoints. Dialogue control management provided by the session layer includes full-duplex, half-duplex, and simplex communications. Session layer management also helps to ensure that multiple streams of data stay synchronized with each other, as in the case of multimedia applications like video conferencing, and assists with the prevention of application related data errors.
The session layer is responsible for creating, maintaining, and tearing down the session.
Three modes are offered:
(Full) Duplex: Both hosts can exchange information simultaneously, independent of each other.
Half Duplex: Hosts can exchange information, but only one host at a time.
Simplex: Only one host can send information to its peer. Information travels in one direction only.
Another aspect of performance that is worthy of some attention is the mode of operation of the network or connection. Obviously, whenever we connect together device A and device B, there must be some way for A to send to B and B to send to A. Many people don’t realize, however, that networking technologies can differ in terms of how these two directions of communication are handled. Depending on how the network is set up, and the characteristics of the technologies used, performance may be improved through the selection of performance-enhancing modes.
Basic Communication Modes of Operation
Let's begin with a look at the three basic modes of operation that can exist for any network connection, communications channel, or interface.
Simplex Operation
In simplex operation, a network cable or communications channel can only send information in one direction; it's a “one-way street”. This may seem counter-intuitive: what's the point of communications that only travel in one direction? In fact, there are at least two different places where simplex operation is encountered in modern networking.
The first is when two distinct channels are used for communication: one transmits from A to B and the other from B to A. This is surprisingly common, even though not always obvious. For example, most if not all fiber optic communication is simplex, using one strand to send data in each direction. But this may not be obvious if the pair of fiber strands are combined into one cable.
Simplex operation is also used in special types of technologies, especially ones that are asymmetric. For example, one type of satellite Internet access sends data over the satellite only for downloads, while a regular dial-up modem is used for upload to the service provider. In this case, both the satellite link and the dial-up connection are operating in a simplex mode.
Half-Duplex Operation
Technologies that employ half-duplex operation are capable of sending information in both directions between two nodes, but only one direction or the other can be utilized at a time. This is a fairly common mode of operation when there is only a single network medium (cable, radio frequency and so forth) between devices.
While this term is often used to describe the behavior of a pair of devices, it can more generally refer to any number of connected devices that take turns transmitting. For example, in conventional Ethernet networks, any device can transmit, but only one may do so at a time. For this reason, regular (unswitched) Ethernet networks are often said to be “half-duplex”, even though it may seem strange to describe a LAN that way.
Full-Duplex Operation
In full-duplex operation, a connection between two devices is capable of sending data in both directions simultaneously. Full-duplex channels can be constructed either as a pair of simplex links (as described above) or using one channel designed to permit bidirectional simultaneous transmissions. A full-duplex link can only connect two devices, so many such links are required if multiple devices are to be connected together.
Note that the term “full-duplex” is somewhat redundant; “duplex” would suffice, but everyone still says “full-duplex” (likely, to differentiate this mode from half-duplex).
For a listing of protocols associated with Layer 5 of the OSI model, see below:
ADSP - AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol
ASP - AppleTalk Session Protocol
H.245 - Call Control Protocol for Multimedia Communication
ISO-SP
OSI session-layer protocol (X.225, ISO 8327)
iSNS - Internet Storage Name Service
The following are incorrect answers:
Synchronous and Asynchronous are not session layer modes.
Half simplex does not exist. By definition, simplex means that information travels one way only, so half-simplex is a oxymoron.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 5603-5636). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_SimplexFullDuplexandHalfDuplexOperation.htm
and
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-session-layer.htm
Several analysis methods can be employed by an IDS, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, and their applicability to any given situation should be carefully considered. There are two basic IDS analysis methods that exists. Which of the basic method is more prone to false positive?
Pattern Matching (also called signature analysis)
Anomaly Detection
Host-based intrusion detection
Network-based intrusion detection
Several analysis methods can be employed by an IDS, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, and their applicability to any given situation should be carefully considered.
There are two basic IDS analysis methods:
1. Pattern Matching (also called signature analysis), and
2. Anomaly detection
PATTERN MATCHING
Some of the first IDS products used signature analysis as their detection method and simply looked for known characteristics of an attack (such as specific packet sequences or text in the data stream) to produce an alert if that pattern was detected. If a new or different attack vector is used, it will not match a known signature and, thus, slip past the IDS.
ANOMALY DETECTION
Alternately, anomaly detection uses behavioral characteristics of a system’s operation or network traffic to draw conclusions on whether the traffic represents a risk to the network or host. Anomalies may include but are not limited to:
Multiple failed log-on attempts
Users logging in at strange hours
Unexplained changes to system clocks
Unusual error messages
Unexplained system shutdowns or restarts
Attempts to access restricted files
An anomaly-based IDS tends to produce more data because anything outside of the expected behavior is reported. Thus, they tend to report more false positives as expected behavior patterns change. An advantage to anomaly-based IDS is that, because they are based on behavior identification and not specific patterns of traffic, they are often able to detect new attacks that may be overlooked by a signature-based system. Often information from an anomaly-based IDS may be used to create a pattern for a signature-based IDS.
Host Based Intrusion Detection (HIDS)
HIDS is the implementation of IDS capabilities at the host level. Its most significant difference from NIDS is that related processes are limited to the boundaries of a single-host system. However, this presents advantages in effectively detecting objectionable activities because the IDS process is running directly on the host system, not just observing it from the network. This offers unfettered access to system logs, processes, system information, and device information, and virtually eliminates limits associated with encryption. The level of integration represented by HIDS increases the level of visibility and control at the disposal of the HIDS application.
Network Based Intrustion Detection (NIDS)
NIDS are usually incorporated into the network in a passive architecture, taking advantage of promiscuous mode access to the network. This means that it has visibility into every packet traversing the network segment. This allows the system to inspect packets and monitor sessions without impacting the network or the systems and applications utilizing the network.
Below you have other ways that instrusion detection can be performed:
Stateful Matching Intrusion Detection
Stateful matching takes pattern matching to the next level. It scans for attack signatures in the context of a stream of traffic or overall system behavior rather than the individual packets or discrete system activities. For example, an attacker may use a tool that sends a volley of valid packets to a targeted system. Because all the packets are valid, pattern matching is nearly useless. However, the fact that a large volume of the packets was seen may, itself, represent a known or potential attack pattern. To evade attack, then, the attacker may send the packets from multiple locations with long wait periods between each transmission to either confuse the signature detection system or exhaust its session timing window. If the IDS service is tuned to record and analyze traffic over a long period of time it may detect such an attack. Because stateful matching also uses signatures, it too must be updated regularly and, thus, has some of the same limitations as pattern matching.
Statistical Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection
The statistical anomaly-based IDS analyzes event data by comparing it to typical, known, or predicted traffic profiles in an effort to find potential security breaches. It attempts to identify suspicious behavior by analyzing event data and identifying patterns of entries that deviate from a predicted norm. This type of detection method can be very effective and, at a very high level, begins to take on characteristics seen in IPS by establishing an expected baseline of behavior and acting on divergence from that baseline. However, there are some potential issues that may surface with a statistical IDS. Tuning the IDS can be challenging and, if not performed regularly, the system will be prone to false positives. Also, the definition of normal traffic can be open to interpretation and does not preclude an attacker from using normal activities to penetrate systems. Additionally, in a large, complex, dynamic corporate environment, it can be difficult, if not impossible, to clearly define “normal” traffic. The value of statistical analysis is that the system has the potential to detect previously unknown attacks. This is a huge departure from the limitation of matching previously known signatures. Therefore, when combined with signature matching technology, the statistical anomaly-based IDS can be very effective.
Protocol Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection
A protocol anomaly-based IDS identifies any unacceptable deviation from expected behavior based on known network protocols. For example, if the IDS is monitoring an HTTP session and the traffic contains attributes that deviate from established HTTP session protocol standards, the IDS may view that as a malicious attempt to manipulate the protocol, penetrate a firewall, or exploit a vulnerability. The value of this method is directly related to the use of well-known or well-defined protocols within an environment. If an organization primarily uses well-known protocols (such as HTTP, FTP, or telnet) this can be an effective method of performing intrusion detection. In the face of custom or nonstandard protocols, however, the system will have more difficulty or be completely unable to determine the proper packet format. Interestingly, this type of method is prone to the same challenges faced by signature-based IDSs. For example, specific protocol analysis modules may have to be added or customized to deal with unique or new protocols or unusual use of standard protocols. Nevertheless, having an IDS that is intimately aware of valid protocol use can be very powerful when an organization employs standard implementations of common protocols.
Traffic Anomaly-Based Intrusion
Detection A traffic anomaly-based IDS identifies any unacceptable deviation from expected behavior based on actual traffic structure. When a session is established between systems, there is typically an expected pattern and behavior to the traffic transmitted in that session. That traffic can be compared to expected traffic conduct based on the understandings of traditional system interaction for that type of connection. Like the other types of anomaly-based IDS, traffic anomaly-based IDS relies on the ability to establish “normal” patterns of traffic and expected modes of behavior in systems, networks, and applications. In a highly dynamic environment it may be difficult, if not impossible, to clearly define these parameters.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3664-3686). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3711-3734). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3694-3711). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following monitors network traffic in real time?
network-based IDS
host-based IDS
application-based IDS
firewall-based IDS
This type of IDS is called a network-based IDS because monitors network traffic in real time.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
What setup should an administrator use for regularly testing the strength of user passwords?
A networked workstation so that the live password database can easily be accessed by the cracking program.
A networked workstation so the password database can easily be copied locally and processed by the cracking program.
A standalone workstation on which the password database is copied and processed by the cracking program.
A password-cracking program is unethical; therefore it should not be used.
Poor password selection is frequently a major security problem for any system's security. Administrators should obtain and use password-guessing programs frequently to identify those users having easily guessed passwords.
Because password-cracking programs are very CPU intensive and can slow the system on which it is running, it is a good idea to transfer the encrypted passwords to a standalone (not networked) workstation. Also, by doing the work on a non-networked machine, any results found will not be accessible by anyone unless they have physical access to that system.
Out of the four choice presented above this is the best choice.
However, in real life you would have strong password policies that enforce complexity requirements and does not let the user choose a simple or short password that can be easily cracked or guessed. That would be the best choice if it was one of the choice presented.
Another issue with password cracking is one of privacy. Many password cracking tools can avoid this by only showing the password was cracked and not showing what the password actually is. It is masking the password being used from the person doing the cracking.
Source: National Security Agency, Systems and Network Attack Center (SNAC), The 60 Minute Network Security Guide, February 2002, page 8.
Which of the following would assist the most in Host Based intrusion detection?
audit trails.
access control lists.
security clearances
host-based authentication
To assist in Intrusion Detection you would review audit logs for access violations.
The following answers are incorrect:
access control lists. This is incorrect because access control lists determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
security clearances. This is incorrect because security clearances determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
host-based authentication. This is incorrect because host-based authentication determine who have been authenticated to the system but do not dectect intrusions.
Which of the following is the BEST way to detect software license violations?
Implementing a corporate policy on copyright infringements and software use.
Requiring that all PCs be diskless workstations.
Installing metering software on the LAN so applications can be accessed through the metered software.
Regularly scanning PCs in use to ensure that unauthorized copies of software have not been loaded on the PC.
The best way to prevent and detect software license violations is to regularly scan used PCs, either from the LAN or directly, to ensure that unauthorized copies of software have not been loaded on the PC.
Other options are not detective.
A corporate policy is not necessarily enforced and followed by all employees.
Software can be installed from other means than floppies or CD-ROMs (from a LAN or even downloaded from the Internet) and software metering only concerns applications that are registered.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, Chapter 3: Technical Infrastructure and Operational Practices (page 108).
Which of the following usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources?
network-based IDS
host-based IDS
application-based IDS
firewall-based IDS
A network-based IDS usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
Who should measure the effectiveness of Information System security related controls in an organization?
The local security specialist
The business manager
The systems auditor
The central security manager
It is the systems auditor that should lead the effort to ensure that the security controls are in place and effective. The audit would verify that the controls comply with polices, procedures, laws, and regulations where applicable. The findings would provide these to senior management.
The following answers are incorrect:
the local security specialist. Is incorrect because an independent review should take place by a third party. The security specialist might offer mitigation strategies but it is the auditor that would ensure the effectiveness of the controls
the business manager. Is incorrect because the business manager would be responsible that the controls are in place, but it is the auditor that would ensure the effectiveness of the controls.
the central security manager. Is incorrect because the central security manager would be responsible for implementing the controls, but it is the auditor that is responsibe for ensuring their effectiveness.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished:
through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function.
through logical or technical controls involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through logical or technical controls but not involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through access control mechanisms that do not require identification and authentication and do not operate through the audit function.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function. These controls must be in accordance with and accurately represent the organization's security policy. Assurance procedures ensure that the control mechanisms correctly implement the security policy for the entire life cycle of an information system.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
Which of the following ciphers is a subset on which the Vigenere polyalphabetic cipher was based on?
Caesar
The Jefferson disks
Enigma
SIGABA
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
The encryption step performed by a Caesar cipher is often incorporated as part of more complex schemes, such as the Vigenère cipher, and still has modern application in the ROT13 system. As with all single alphabet substitution ciphers, the Caesar cipher is easily broken and in modern practice offers essentially no communication security.
The following answer were incorrect:
The Jefferson disk, or wheel cipher as Thomas Jefferson named it, also known as the Bazeries Cylinder, is a cipher system using a set of wheels or disks, each with the 26 letters of the alphabet arranged around their edge. The order of the letters is different for each disk and is usually scrambled in some random way. Each disk is marked with a unique number. A hole in the centre of the disks allows them to be stacked on an axle. The disks are removable and can be mounted on the axle in any order desired. The order of the disks is the cipher key, and both sender and receiver must arrange the disks in the same predefined order. Jefferson's device had 36 disks.
An Enigma machine is any of a family of related electro-mechanical rotor cipher machines used for the encryption and decryption of secret messages. Enigma was invented by the German engineer Arthur Scherbius at the end of World War I. The early models were used commercially from the early 1920s, and adopted by military and government services of several countries. Several different Enigma models were produced, but the German military models are the ones most commonly discussed.
SIGABA: In the history of cryptography, the ECM Mark II was a cipher machine used by the United States for message encryption from World War II until the 1950s. The machine was also known as the SIGABA or Converter M-134 by the Army, or CSP-888/889 by the Navy, and a modified Navy version was termed the CSP-2900. Like many machines of the era it used an electromechanical system of rotors in order to encipher messages, but with a number of security improvements over previous designs. No successful cryptanalysis of the machine during its service lifetime is publicly known.
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jefferson_disk
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sigaba
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enigma_machine
Which of the following is NOT a symmetric key algorithm?
Blowfish
Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
Triple DES (3DES)
RC5
Digital Signature Standard (DSS) specifies a Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) appropriate for applications requiring a digital signature, providing the capability to generate signatures (with the use of a private key) and verify them (with the use of the corresponding public key).
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 550).
Which of the following elements is NOT included in a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
Timestamping
Repository
Certificate revocation
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
Other elements are included in a PKI.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 165).
Which of the following is a cryptographic protocol and infrastructure developed to send encrypted credit card numbers over the Internet?
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
MONDEX
Secure Shell (SSH-2)
Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (S-HTTP)
SET was developed by a consortium including Visa and MasterCard.
Source: Harris, Shon, CISSP All In One Exam Guide, pages 668-669.
Mondex is a smart card electronic cash system owned by MasterCard.
SSH-2 is a secure, efficient, and portable version of SSH (Secure Shell) which is a secure replacement for telnet.
Secure HTTP is a secure message-oriented communications protocol designed for use in conjunction with HTTP. It is designed to coexist with HTTP's messaging model and to be easily integrated with HTTP applications.
Which of the following statements pertaining to message digests is incorrect?
The original file cannot be created from the message digest.
Two different files should not have the same message digest.
The message digest should be calculated using at least 128 bytes of the file.
Messages digests are usually of fixed size.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 160).
Which of the following services is NOT provided by the digital signature standard (DSS)?
Encryption
Integrity
Digital signature
Authentication
DSS provides Integrity, digital signature and Authentication, but does not provide Encryption.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 160).
What is the maximum allowable key size of the Rijndael encryption algorithm?
128 bits
192 bits
256 bits
512 bits
The Rijndael algorithm, chosen as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to replace DES, can be categorized as an iterated block cipher with a variable block length and key length that can be independently chosen as 128, 192 or 256 bits.
Below you have a summary of the differences between AES and Rijndael.
AES is the advanced encryption standard defined by FIPS 197. It is implemented differently than Rijndael:
FIPS-197 specifies that the block size must always be 128 bits in AES, and that the key size may be either 128, 192, or 256 bits. Therefore AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256 are actually:
Key Size (bits) Number of rounds
Block Size (bits)
AES-128
128 10 Rounds
128
AES-192
192 12 Rounds
128
AES-256
256 14 Rounds
128
Some book will say "up to 9 rounds will be done with a 128 bits keys". Really it is 10 rounds because you must include round zero which is the first round.
By contrast, the Rijndael specification per se is specified with block and key sizes that may be any multiple of 32 bits, both with a minimum of 128 and a maximum of 256 bits.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 153).
and
FIPS 197
and
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard
What algorithm was DES derived from?
Twofish.
Skipjack.
Brooks-Aldeman.
Lucifer.
NSA took the 128-bit algorithm Lucifer that IBM developed, reduced the key size to 64 bits and with that developed DES.
The following answers are incorrect:
Twofish. This is incorrect because Twofish is related to Blowfish as a possible replacement for DES.
Skipjack. This is incorrect, Skipjack was developed after DES by the NSA .
Brooks-Aldeman. This is incorrect because this is a distractor, no algorithm exists with this name.
What key size is used by the Clipper Chip?
40 bits
56 bits
64 bits
80 bits
The Clipper Chip is a NSA designed tamperproof chip for encrypting data and it uses the SkipJack algorithm. Each Clipper Chip has a unique serial number and a copy of the unit key is stored in the database under this serial number. The sending Clipper Chip generates and sends a Law Enforcement Access Field (LEAF) value included in the transmitted message. It is based on a 80-bit key and a 16-bit checksum.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#5 Cryptography (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 1).
Brute force attacks against encryption keys have increased in potency because of increased computing power. Which of the following is often considered a good protection against the brute force cryptography attack?
The use of good key generators.
The use of session keys.
Nothing can defend you against a brute force crypto key attack.
Algorithms that are immune to brute force key attacks.
If we assume a crytpo-system with a large key (and therefore a large key space) a brute force attack will likely take a good deal of time - anywhere from several hours to several years depending on a number of variables. If you use a session key for each message you encrypt, then the brute force attack provides the attacker with only the key for that one message. So, if you are encrypting 10 messages a day, each with a different session key, but it takes me a month to break each session key then I am fighting a loosing battle.
The other answers are not correct because:
"The use of good key generators" is not correct because a brute force key attack will eventually run through all possible combinations of key. Therefore, any key will eventually be broken in this manner given enough time.
"Nothing can defend you against a brute force crypto key attack" is incorrect, and not the best answer listed. While it is technically true that any key will eventually be broken by a brute force attack, the question remains "how long will it take?". In other words, if you encrypt something today but I can't read it for 10,000 years, will you still care? If the key is changed every session does it matter if it can be broken after the session has ended? Of the answers listed here, session keys are "often considered a good protection against the brute force cryptography attack" as the question asks.
"Algorithms that are immune to brute force key attacks" is incorrect because there currently are no such algorithms.
References:
Official ISC2 Guide page: 259
All in One Third Edition page: 623
What can be defined as an instance of two different keys generating the same ciphertext from the same plaintext?
Key collision
Key clustering
Hashing
Ciphertext collision
Key clustering happens when a plaintext message generates identical ciphertext messages using the same transformation algorithm, but with different keys.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 130).
The Diffie-Hellman algorithm is used for:
Encryption
Digital signature
Key agreement
Non-repudiation
The Diffie-Hellman algorithm is used for Key agreement (key distribution) and cannot be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#5 Cryptography (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 4).
Note: key agreement, is different from key exchange, the functionality used by the other asymmetric algorithms.
References:
AIO, third edition Cryptography (Page 632)
AIO, fourth edition Cryptography (Page 709)
You work in a police department forensics lab where you examine computers for evidence of crimes. Your work is vital to the success of the prosecution of criminals.
One day you receive a laptop and are part of a two man team responsible for examining it together. However, it is lunch time and after receiving the laptop you leave it on your desk and you both head out to lunch.
What critical step in forensic evidence have you forgotten?
Chain of custody
Locking the laptop in your desk
Making a disk image for examination
Cracking the admin password with chntpw
When evidence from a crime is to be used in the prosecution of a criminal it is critical that you follow the law when handling that evidence. Part of that process is called chain of custody and is when you maintain proactive and documented control over ALL evidence involved in a crime.
Failure to do this can lead to the dismissal of charges against a criminal because if the evidence is compromised because you failed to maintain of chain of custody.
A chain of custody is chronological documentation for evidence in a particular case, and is especially important with electronic evidence due to the possibility of fraudulent data alteration, deletion, or creation. A fully detailed chain of custody report is necessary to prove the physical custody of a piece of evidence and show all parties that had access to said evidence at any given time.
Evidence must be protected from the time it is collected until the time it is presented in court.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Locking the laptop in your desk: Even this wouldn't assure that the defense team would try to challenge chain of custody handling. It's usually easy to break into a desk drawer and evidence should be stored in approved safes or other storage facility.
- Making a disk image for examination: This is a key part of system forensics where we make a disk image of the evidence system and study that as opposed to studying the real disk drive. That could lead to loss of evidence. However if the original evidence is not secured than the chain of custoday has not been maintained properly.
- Cracking the admin password with chntpw: This isn't correct. Your first mistake was to compromise the chain of custody of the laptop. The chntpw program is a Linux utility to (re)set the password of any user that has a valid (local) account on a Windows system, by modifying the crypted password in the registry's SAM file. You do not need to know the old password to set a new one. It works offline which means you must have physical access (i.e., you have to shutdown your computer and boot off a linux floppy disk). The bootdisk includes stuff to access NTFS partitions and scripts to glue the whole thing together. This utility works with SYSKEY and includes the option to turn it off. A bootdisk image is provided on their website at http://freecode.com/projects/chntpw .
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
For more details and to cover 100% of the exam QUESTION NO: s, subscribe to our holistic Security+ 2014 CBT Tutorial at: http://www.cccure.tv/
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chain_of_custody
and
http://www.datarecovery.com/forensic_chain_of_custody.asp
In a SSL session between a client and a server, who is responsible for generating the master secret that will be used as a seed to generate the symmetric keys that will be used during the session?
Both client and server
The client's browser
The web server
The merchant's Certificate Server
Once the merchant server has been authenticated by the browser client, the browser generates a master secret that is to be shared only between the server and client. This secret serves as a seed to generate the session (private) keys. The master secret is then encrypted with the merchant's public key and sent to the server. The fact that the master secret is generated by the client's browser provides the client assurance that the server is not reusing keys that would have been used in a previous session with another client.
Source: ANDRESS, Mandy, Exam Cram CISSP, Coriolis, 2001, Chapter 6: Cryptography (page 112).
Also: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2001, page 569.
Which of the following is NOT a true statement regarding the implementaton of the 3DES modes?
DES-EEE1 uses one key
DES-EEE2 uses two keys
DES-EEE3 uses three keys
DES-EDE2 uses two keys
There is no DES mode call DES-EEE1. It does not exist.
The following are the correct modes for triple-DES (3DES):
DES-EEE3 uses three keys for encryption and the data is encrypted, encrypted, encrypted;
DES-EDE3 uses three keys and encrypts, decrypts and encrypts data.
DES-EEE2 and DES-EDE2 are the same as the previous modes, but the first and third operations use the same key.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Shon Harris, CISSP All In One (AIO) book, 6th edition , page 808
and
Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, 2nd Edition (2010) , page 344-345
Which of the following ASYMMETRIC encryption algorithms is based on the difficulty of FACTORING LARGE NUMBERS?
El Gamal
Elliptic Curve Cryptosystems (ECCs)
RSA
International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA)
Named after its inventors Ron Rivest , Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman is based on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers.
Factoring a number means representing it as the product of prime numbers. Prime numbers, such as 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and 13, are those numbers that are not evenly divisible by any smaller number, except 1. A non-prime, or composite number, can be written as the product of smaller primes, known as its prime factors. 665, for example is the product of the primes 5, 7, and 19. A number is said to be factored when all of its prime factors are identified. As the size of the number increases, the difficulty of factoring increases rapidly.
The other answers are incorrect because:
El Gamal is based on the discrete logarithms in a finite field.
Elliptic Curve Cryptosystems (ECCs) computes discrete logarithms of elliptic curves.
International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) is a block cipher and operates on 64 bit blocks of data and is a SYMMETRIC algorithm.
Reference : Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter-8 : Cryptography , Page : 638
What can be defined as secret communications where the very existence of the message is hidden?
Clustering
Steganography
Cryptology
Vernam cipher
Steganography is a secret communication where the very existence of the message is hidden. For example, in a digital image, the least significant bit of each word can be used to comprise a message without causing any significant change in the image. Key clustering is a situation in which a plaintext message generates identical ciphertext messages using the same transformation algorithm but with different keys. Cryptology encompasses cryptography and cryptanalysis. The Vernam Cipher, also called a one-time pad, is an encryption scheme using a random key of the same size as the message and is used only once. It is said to be unbreakable, even with infinite resources.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 134).
Which of the following statements pertaining to stream ciphers is correct?
A stream cipher is a type of asymmetric encryption algorithm.
A stream cipher generates what is called a keystream.
A stream cipher is slower than a block cipher.
A stream cipher is not appropriate for hardware-based encryption.
A stream cipher is a type of symmetric encryption algorithm that operates on continuous streams of plain text and is appropriate for hardware-based encryption.
Stream ciphers can be designed to be exceptionally fast, much faster than any block cipher. A stream cipher generates what is called a keystream (a sequence of bits used as a key).
Stream ciphers can be viewed as approximating the action of a proven unbreakable cipher, the one-time pad (OTP), sometimes known as the Vernam cipher. A one-time pad uses a keystream of completely random digits. The keystream is combined with the plaintext digits one at a time to form the ciphertext. This system was proved to be secure by Claude Shannon in 1949. However, the keystream must be (at least) the same length as the plaintext, and generated completely at random. This makes the system very cumbersome to implement in practice, and as a result the one-time pad has not been widely used, except for the most critical applications.
A stream cipher makes use of a much smaller and more convenient key — 128 bits, for example. Based on this key, it generates a pseudorandom keystream which can be combined with the plaintext digits in a similar fashion to the one-time pad. However, this comes at a cost: because the keystream is now pseudorandom, and not truly random, the proof of security associated with the one-time pad no longer holds: it is quite possible for a stream cipher to be completely insecure if it is not implemented properly as we have seen with the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol.
Encryption is accomplished by combining the keystream with the plaintext, usually with the bitwise XOR operation.
Source: DUPUIS, Clement, CISSP Open Study Guide on domain 5, cryptography, April 1999.
More details can be obtained on Stream Ciphers in RSA Security's FAQ on Stream Ciphers.
What does the (star) integrity axiom mean in the Biba model?
No read up
No write down
No read down
No write up
The (star) integrity axiom of the Biba access control model states that an object at one level of integrity is not permitted to modify an object of a higher level of integrity (no write up).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 5: Security Architectures and Models (page 205).
What security model is dependent on security labels?
Discretionary access control
Label-based access control
Mandatory access control
Non-discretionary access control
With mandatory access control (MAC), the authorization of a subject's access to an object is dependant upon labels, which indicate the subject's clearance, and the classification or sensitivity of the object. Label-based access control is not defined.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 33).
Which access control model is best suited in an environment where a high security level is required and where it is desired that only the administrator grants access control?
DAC
MAC
Access control matrix
TACACS
MAC provides high security by regulating access based on the clearance of individual users and sensitivity labels for each object. Clearance levels and sensitivity levels cannot be modified by individual users -- for example, user Joe (SECRET clearance) cannot reclassify the "Presidential Doughnut Recipe" from "SECRET" to "CONFIDENTIAL" so that his friend Jane (CONFIDENTIAL clearance) can read it. The administrator is ultimately responsible for configuring this protection in accordance with security policy and directives from the Data Owner.
DAC is incorrect. In DAC, the data owner is responsible for controlling access to the object.
Access control matrix is incorrect. The access control matrix is a way of thinking about the access control needed by a population of subjects to a population of objects. This access control can be applied using rules, ACL's, capability tables, etc.
TACACS is incorrect. TACACS is a tool for performing user authentication.
References:
CBK, p. 187, Domain 2: Access Control.
AIO3, Chapter 4, Access Control.
Rule-Based Access Control (RuBAC) access is determined by rules. Such rules would fit within what category of access control ?
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
Mandatory Access control (MAC)
Non-Discretionary Access Control (NDAC)
Lattice-based Access control
Rule-based access control is a type of non-discretionary access control because this access is determined by rules and the subject does not decide what those rules will be, the rules are uniformly applied to ALL of the users or subjects.
In general, all access control policies other than DAC are grouped in the category of non-discretionary access control (NDAC). As the name implies, policies in this category have rules that are not established at the discretion of the user. Non-discretionary policies establish controls that cannot be changed by users, but only through administrative action.
Both Role Based Access Control (RBAC) and Rule Based Access Control (RuBAC) fall within Non Discretionary Access Control (NDAC). If it is not DAC or MAC then it is most likely NDAC.
IT IS NOT ALWAYS BLACK OR WHITE
The different access control models are not totally exclusive of each others. MAC is making use of Rules to be implemented. However with MAC you have requirements above and beyond having simple access rules. The subject would get formal approval from management, the subject must have the proper security clearance, objects must have labels/sensitivity levels attached to them, subjects must have the proper security clearance. If all of this is in place then you have MAC.
BELOW YOU HAVE A DESCRIPTION OF THE DIFFERENT CATEGORIES:
MAC = Mandatory Access Control
Under a mandatory access control environment, the system or security administrator will define what permissions subjects have on objects. The administrator does not dictate user’s access but simply configure the proper level of access as dictated by the Data Owner.
The MAC system will look at the Security Clearance of the subject and compare it with the object sensitivity level or classification level. This is what is called the dominance relationship.
The subject must DOMINATE the object sensitivity level. Which means that the subject must have a security clearance equal or higher than the object he is attempting to access.
MAC also introduce the concept of labels. Every objects will have a label attached to them indicating the classification of the object as well as categories that are used to impose the need to know (NTK) principle. Even thou a user has a security clearance of Secret it does not mean he would be able to access any Secret documents within the system. He would be allowed to access only Secret document for which he has a Need To Know, formal approval, and object where the user belong to one of the categories attached to the object.
If there is no clearance and no labels then IT IS NOT Mandatory Access Control.
Many of the other models can mimic MAC but none of them have labels and a dominance relationship so they are NOT in the MAC category.
NISTR-7316 Says:
Usually a labeling mechanism and a set of interfaces are used to determine access based on the MAC policy; for example, a user who is running a process at the Secret classification should not be allowed to read a file with a label of Top Secret. This is known as the “simple security rule,” or “no read up.” Conversely, a user who is running a process with a label of Secret should not be allowed to write to a file with a label of Confidential. This rule is called the “*-property” (pronounced “star property”) or “no write down.” The *-property is required to maintain system security in an automated environment. A variation on this rule called the “strict *-property” requires that information can be written at, but not above, the subject’s clearance level. Multilevel security models such as the Bell-La Padula Confidentiality and Biba Integrity models are used to formally specify this kind of MAC policy.
DAC = Discretionary Access Control
DAC is also known as: Identity Based access control system.
The owner of an object is define as the person who created the object. As such the owner has the discretion to grant access to other users on the network. Access will be granted based solely on the identity of those users.
Such system is good for low level of security. One of the major problem is the fact that a user who has access to someone's else file can further share the file with other users without the knowledge or permission of the owner of the file. Very quickly this could become the wild wild west as there is no control on the dissimination of the information.
RBAC = Role Based Access Control
RBAC is a form of Non-Discretionary access control.
Role Based access control usually maps directly with the different types of jobs performed by employees within a company.
For example there might be 5 security administrator within your company. Instead of creating each of their profile one by one, you would simply create a role and assign the administrators to the role. Once an administrator has been assigned to a role, he will IMPLICITLY inherit the permissions of that role.
RBAC is great tool for environment where there is a a large rotation of employees on a daily basis such as a very large help desk for example.
RBAC or RuBAC = Rule Based Access Control
RuBAC is a form of Non-Discretionary access control.
A good example of a Rule Based access control device would be a Firewall. A single set of rules is imposed to all users attempting to connect through the firewall.
NOTE FROM CLEMENT:
Lot of people tend to confuse MAC and Rule Based Access Control.
Mandatory Access Control must make use of LABELS. If there is only rules and no label, it cannot be Mandatory Access Control. This is why they call it Non Discretionary Access control (NDAC).
There are even books out there that are WRONG on this subject. Books are sometimes opiniated and not strictly based on facts.
In MAC subjects must have clearance to access sensitive objects. Objects have labels that contain the classification to indicate the sensitivity of the object and the label also has categories to enforce the need to know.
Today the best example of rule based access control would be a firewall. All rules are imposed globally to any user attempting to connect through the device. This is NOT the case with MAC.
I strongly recommend you read carefully the following document:
NISTIR-7316 at http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistir/7316/NISTIR-7316.pdf
It is one of the best Access Control Study document to prepare for the exam. Usually I tell people not to worry about the hundreds of NIST documents and other reference. This document is an exception. Take some time to read it.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
and
NISTIR-7316 at http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistir/7316/NISTIR-7316.pdf
and
Conrad, Eric; Misenar, Seth; Feldman, Joshua (2012-09-01). CISSP Study Guide (Kindle Locations 651-652). Elsevier Science (reference). Kindle Edition.
Which integrity model defines a constrained data item, an integrity verification procedure and a transformation procedure?
The Take-Grant model
The Biba integrity model
The Clark Wilson integrity model
The Bell-LaPadula integrity model
The Clark Wilson integrity model addresses the three following integrity goals: 1) data is protected from modification by unauthorized users; 2) data is protected from unauthorized modification by authorized users; and 3) data is internally and externally consistent. It also defines a Constrained Data Item (CDI), an Integrity Verification Procedure (IVP), a Transformation Procedure (TP) and an Unconstrained Data item. The Bell-LaPadula and Take-Grant models are not integrity models.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 5: Security Architecture and Models (page 205).
Which of the following security models does NOT concern itself with the flow of data?
The information flow model
The Biba model
The Bell-LaPadula model
The noninterference model
The goal of a noninterference model is to strictly separate differing security levels to assure that higher-level actions do not determine what lower-level users can see. This is in contrast to other security models that control information flows between differing levels of users, By maintaining strict separation of security levels, a noninterference model minimizes leakages that might happen through a covert channel.
The Bell-LaPadula model is incorrect. The Bell-LaPadula model is concerned with confidentiality and bases access control decsions on the classfication of objects and the clearences of subjects.
The information flow model is incorrect. The information flow models have a similar framework to the Bell-LaPadula model and control how information may flow between objects based on security classes.
The Biba model is incorrect. The Biba model is concerned with integrity and is a complement to the Bell-LaPadula model in that higher levels of integrity are more trusted than lower levels. Access control us based on these integrity levels to assure that read/write operations do not decrease an object's integrity.
References:
CBK, pp 325 - 326
AIO3, pp. 290 - 291
In the context of Biometric authentication, what is a quick way to compare the accuracy of devices. In general, the device that have the lowest value would be the most accurate. Which of the following would be used to compare accuracy of devices?
the CER is used.
the FRR is used
the FAR is used
the FER is used
equal error rate or crossover error rate (EER or CER): the rate at which both accept and reject errors are equal. The value of the EER can be easily obtained from the ROC curve. The EER is a quick way to compare the accuracy of devices with different ROC curves. In general, the device with the lowest EER is most accurate.
In the context of Biometric Authentication almost all types of detection permit a system's sensitivity to be increased or decreased during an inspection process. If the system's sensitivity is increased, such as in an airport metal detector, the system becomes increasingly selective and has a higher False Reject Rate (FRR).
Conversely, if the sensitivity is decreased, the False Acceptance Rate (FAR) will increase.
Thus, to have a valid measure of the system performance, the CrossOver Error Rate (CER) is used.
The following are used as performance metrics for biometric systems:
false accept rate or false match rate (FAR or FMR): the probability that the system incorrectly matches the input pattern to a non-matching template in the database. It measures the percent of invalid inputs which are incorrectly accepted. In case of similarity scale, if the person is imposter in real, but the matching score is higher than the threshold, then he is treated as genuine that increase the FAR and hence performance also depends upon the selection of threshold value.
false reject rate or false non-match rate (FRR or FNMR): the probability that the system fails to detect a match between the input pattern and a matching template in the database. It measures the percent of valid inputs which are incorrectly rejected.
failure to enroll rate (FTE or FER): the rate at which attempts to create a template from an input is unsuccessful. This is most commonly caused by low quality inputs.
failure to capture rate (FTC): Within automatic systems, the probability that the system fails to detect a biometric input when presented correctly.
template capacity: the maximum number of sets of data which can be stored in the system.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 37.
and
Wikipedia at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometrics
In the context of access control, locks, gates, guards are examples of which of the following?
Administrative controls
Technical controls
Physical controls
Logical controls
Administrative, technical and physical controls are categories of access control mechanisms.
Logical and Technical controls are synonymous. So both of them could be eliminated as possible choices.
Physical Controls: These are controls to protect the organization’s people and physical environment, such as locks, gates, and guards. Physical controls may be called “operational controls” in some contexts.
Physical security covers a broad spectrum of controls to protect the physical assets (primarily the people) in an organization. Physical Controls are sometimes referred to as “operational” controls in some risk management frameworks. These controls range from doors, locks, and windows to environment controls, construction standards, and guards. Typically, physical security is based on the notion of establishing security zones or concentric areas within a facility that require increased security as you get closer to the valuable assets inside the facility. Security zones are the physical representation of the defense-in-depth principle discussed earlier in this chapter. Typically, security zones are associated with rooms, offices, floors, or smaller elements, such as a cabinet or storage locker. The design of the physical security controls within the facility must take into account the protection of the asset as well as the individuals working in that area.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 1301-1303). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 1312-1318). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
What is called the percentage at which the False Rejection Rate equals the False Acceptance Rate?
False Rejection Rate (FRR) or Type I Error
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) or Type II Error
Crossover Error Rate (CER)
Failure to enroll rate (FTE or FER)
The percentage at which the False Rejection Rate equals the False Acceptance Rate is called the Crossover Error Rate (CER). Another name for the CER is the Equal Error Rate (EER), any of the two terms could be used.
Equal error rate or crossover error rate (EER or CER)
It is the rate at which both accept and reject errors are equal. The EER is a quick way to compare the accuracy of devices with different ROC curves. In general, the device with the lowest EER is most accurate.
The other choices were all wrong answers:
The following are used as performance metrics for biometric systems:
false accept rate or false match rate (FAR or FMR): the probability that the system incorrectly matches the input pattern to a non-matching template in the database. It measures the percent of invalid inputs which are incorrectly accepted. This is when an impostor would be accepted by the system.
False reject rate or false non-match rate (FRR or FNMR): the probability that the system fails to detect a match between the input pattern and a matching template in the database. It measures the percent of valid inputs which are incorrectly rejected. This is when a valid company employee would be rejected by the system.
Failure to enroll rate (FTE or FER): the rate at which attempts to create a template from an input is unsuccessful. This is most commonly caused by low quality inputs.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 38.
and
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometrics
How would nonrepudiation be best classified as?
A preventive control
A logical control
A corrective control
A compensating control
Systems accountability depends on the ability to ensure that senders cannot deny sending information and that receivers cannot deny receiving it. Because the mechanisms implemented in nonrepudiation prevent the ability to successfully repudiate an action, it can be considered as a preventive control.
Source: STONEBURNER, Gary, NIST Special Publication 800-33: Underlying Technical Models for Information Technology Security, National Institute of Standards and Technology, December 2001, page 7.
Which of the following statements pertaining to RADIUS is incorrect:
A RADIUS server can act as a proxy server, forwarding client requests to other authentication domains.
Most of RADIUS clients have a capability to query secondary RADIUS servers for redundancy.
Most RADIUS servers have built-in database connectivity for billing and reporting purposes.
Most RADIUS servers can work with DIAMETER servers.
This is the correct answer because it is FALSE.
Diameter is an AAA protocol, AAA stands for authentication, authorization and accounting protocol for computer networks, and it is a successor to RADIUS.
The name is a pun on the RADIUS protocol, which is the predecessor (a diameter is twice the radius).
The main differences are as follows:
Reliable transport protocols (TCP or SCTP, not UDP)
The IETF is in the process of standardizing TCP Transport for RADIUS
Network or transport layer security (IPsec or TLS)
The IETF is in the process of standardizing Transport Layer Security for RADIUS
Transition support for RADIUS, although Diameter is not fully compatible with RADIUS
Larger address space for attribute-value pairs (AVPs) and identifiers (32 bits instead of 8 bits)
Client–server protocol, with exception of supporting some server-initiated messages as well
Both stateful and stateless models can be used
Dynamic discovery of peers (using DNS SRV and NAPTR)
Capability negotiation
Supports application layer acknowledgements, defines failover methods and state machines (RFC 3539)
Error notification
Better roaming support
More easily extended; new commands and attributes can be defined
Aligned on 32-bit boundaries
Basic support for user-sessions and accounting
A Diameter Application is not a software application, but a protocol based on the Diameter base protocol (defined in RFC 3588). Each application is defined by an application identifier and can add new command codes and/or new mandatory AVPs. Adding a new optional AVP does not require a new application.
Examples of Diameter applications:
Diameter Mobile IPv4 Application (MobileIP, RFC 4004)
Diameter Network Access Server Application (NASREQ, RFC 4005)
Diameter Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Application (RFC 4072)
Diameter Credit-Control Application (DCCA, RFC 4006)
Diameter Session Initiation Protocol Application (RFC 4740)
Various applications in the 3GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem
All of the other choices presented are true. So Diameter is backwork compatible with Radius (to some extent) but the opposite is false.
Reference(s) used for this question:
TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, MICKI, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th Edition, Volume 2, 2001, CRC Press, NY, Page 38.
and
https://secure.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/wiki/Diameter_%28protocol%29
Which of the following biometric characteristics cannot be used to uniquely authenticate an individual's identity?
Retina scans
Iris scans
Palm scans
Skin scans
The following are typical biometric characteristics that are used to uniquely authenticate an individual's identity:
Fingerprints
Retina scans
Iris scans
Facial scans
Palm scans
Hand geometry
Voice
Handwritten signature dynamics
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 39.
And: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 4: Access Control (pages 127-131).
Which of the following questions is less likely to help in assessing identification and authentication controls?
Is a current list maintained and approved of authorized users and their access?
Are passwords changed at least every ninety days or earlier if needed?
Are inactive user identifications disabled after a specified period of time?
Is there a process for reporting incidents?
Identification and authentication is a technical measure that prevents unauthorized people (or unauthorized processes) from entering an IT system. Access control usually requires that the system be able to identify and differentiate among users. Reporting incidents is more related to incident response capability (operational control) than to identification and authentication (technical control).
Source: SWANSON, Marianne, NIST Special Publication 800-26, Security Self-Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems, November 2001 (Pages A-30 to A-32).
Which type of password provides maximum security because a new password is required for each new log-on?
One-time or dynamic password
Congnitive password
Static password
Passphrase
"one-time password" provides maximum security because a new password is required for each new log-on.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 36.
Which type of control is concerned with avoiding occurrences of risks?
Deterrent controls
Detective controls
Preventive controls
Compensating controls
Preventive controls are concerned with avoiding occurrences of risks while deterrent controls are concerned with discouraging violations. Detecting controls identify occurrences and compensating controls are alternative controls, used to compensate weaknesses in other controls. Supervision is an example of compensating control.
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
What is the main objective of proper separation of duties?
To prevent employees from disclosing sensitive information.
To ensure access controls are in place.
To ensure that no single individual can compromise a system.
To ensure that audit trails are not tampered with.
The primary objective of proper separation of duties is to ensure that one person acting alone cannot compromise the company's security in any way. A proper separation of duties does not prevent employees from disclosing information, nor does it ensure that access controls are in place or that audit trails are not tampered with.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 12: Operations Security (Page 808).
Another type of access control is lattice-based access control. In this type of control a lattice model is applied. How is this type of access control concept applied?
The pair of elements is the subject and object, and the subject has an upper bound equal or higher than the upper bound of the object being accessed.
The pair of elements is the subject and object, and the subject has an upper bound lower then the upper bound of the object being accessed.
The pair of elements is the subject and object, and the subject has no special upper or lower bound needed within the lattice.
The pair of elements is the subject and object, and the subject has no access rights in relation to an object.
To apply this concept to access control, the pair of elements is the subject and object, and the subject has to have an upper bound equal or higher than the object being accessed.
WIKIPEDIA has a great explanation as well:
In computer security, lattice-based access control (LBAC) is a complex access control based on the interaction between any combination of objects (such as resources, computers, and applications) and subjects (such as individuals, groups or organizations).
In this type of label-based mandatory access control model, a lattice is used to define the levels of security that an object may have and that a subject may have access to. The subject is only allowed to access an object if the security level of the subject is greater than or equal to that of the object.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 34.
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lattice-based_access_control
When submitting a passphrase for authentication, the passphrase is converted into ...
a virtual password by the system
a new passphrase by the system
a new passphrase by the encryption technology
a real password by the system which can be used forever
Passwords can be compromised and must be protected. In the ideal case, a password should only be used once. The changing of passwords can also fall between these two extremes.
Passwords can be required to change monthly, quarterly, or at other intervals, depending on the criticality of the information needing protection and the password's frequency of use.
Obviously, the more times a password is used, the more chance there is of it being compromised.
It is recommended to use a passphrase instead of a password. A passphrase is more resistant to attacks. The passphrase is converted into a virtual password by the system. Often time the passphrase will exceed the maximum length supported by the system and it must be trucated into a Virtual Password.
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://www.itl.nist.gov/fipspubs/fip112.htm
and
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 36 & 37.
In non-discretionary access control using Role Based Access Control (RBAC), a central authority determines what subjects can have access to certain objects based on the organizational security policy. The access controls may be based on:
The societies role in the organization
The individual's role in the organization
The group-dynamics as they relate to the individual's role in the organization
The group-dynamics as they relate to the master-slave role in the organization
In Non-Discretionary Access Control, when Role Based Access Control is being used, a central authority determines what subjects can have access to certain objects based on the organizational security policy. The access controls may be based on the individual's role in the organization.
Reference(S) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
Which of the following statements pertaining to the Bell-LaPadula is TRUE if you are NOT making use of the strong star property?
It allows "read up."
It addresses covert channels.
It addresses management of access controls.
It allows "write up."
Bell–LaPadula Confidentiality Model10 The Bell–LaPadula model is perhaps the most well-known and significant security model, in addition to being one of the oldest models used in the creation of modern secure computing systems. Like the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (or TCSEC), it was inspired by early U.S. Department of Defense security policies and the need to prove that confidentiality could be maintained. In other words, its primary goal is to prevent disclosure as the model system moves from one state (one point in time) to another.
When the strong star property is not being used it means that both the property and the Simple Security Property rules would be applied.
The Star (*) property rule of the Bell-LaPadula model says that subjects cannot write down, this would compromise the confidentiality of the information if someone at the secret layer would write the object down to a confidential container for example.
The Simple Security Property rule states that the subject cannot read up which means that a subject at the secret layer would not be able to access objects at Top Secret for example.
You must remember: The model tells you about are NOT allowed to do. Anything else would be allowed. For example within the Bell LaPadula model you would be allowed to write up as it does not compromise the security of the information. In fact it would upgrade it to the point that you could lock yourself out of your own information if you have only a secret security clearance.
The following are incorrect answers because they are all FALSE:
"It allows read up" is incorrect. The "simple security" property forbids read up.
"It addresses covert channels" is incorrect. Covert channels are not addressed by the Bell-LaPadula model.
"It addresses management of access controls" is incorrect. Management of access controls are beyond the scope of the Bell-LaPadula model.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 17595-17600). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
This baseline sets certain thresholds for specific errors or mistakes allowed and the amount of these occurrences that can take place before it is considered suspicious?
Checkpoint level
Ceiling level
Clipping level
Threshold level
Organizations usually forgive a particular type, number, or pattern of violations, thus permitting a predetermined number of user errors before gathering this data for analysis. An organization attempting to track all violations, without sophisticated statistical computing ability, would be unable to manage the sheer quantity of such data. To make a violation listing effective, a clipping level must be established.
The clipping level establishes a baseline for violation activities that may be normal user errors. Only after this baseline is exceeded is a violation record produced. This solution is particularly effective for small- to medium-sized installations. Organizations with large-scale computing facilities often track all violations and use statistical routines to cull out the minor infractions (e.g., forgetting a password or mistyping it several times).
If the number of violations being tracked becomes unmanageable, the first step in correcting the problems should be to analyze why the condition has occurred. Do users understand how they are to interact with the computer resource? Are the rules too difficult to follow? Violation tracking and analysis can be valuable tools in assisting an organization to develop thorough but useable controls. Once these are in place and records are produced that accurately reflect serious violations, tracking and analysis become the first line of defense. With this procedure, intrusions are discovered before major damage occurs and sometimes early enough to catch the perpetrator. In addition, business protection and preservation are strengthened.
The following answers are incorrect:
All of the other choices presented were simply detractors.
The following reference(s) were used for this question:
Handbook of Information Security Management
Which of the following protects a password from eavesdroppers and supports the encryption of communication?
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
Challenge Handshake Identification Protocol (CHIP)
Challenge Handshake Encryption Protocol (CHEP)
Challenge Handshake Substitution Protocol (CHSP)
CHAP: A protocol that uses a three way hanbdshake The server sends the client a challenge which includes a random value(a nonce) to thwart replay attacks. The client responds with the MD5 hash of the nonce and the password.
The authentication is successful if the client's response is the one that the server expected.
Which of the following access control models requires defining classification for objects?
Role-based access control
Discretionary access control
Identity-based access control
Mandatory access control
With mandatory access control (MAC), the authorization of a subject's access to an object is dependant upon labels, which indicate the subject's clearance, and classification of objects.
The Following answers were incorrect:
Identity-based Access Control is a type of Discretionary Access Control (DAC), they are synonymous.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) and Rule Based Access Control (RuBAC or RBAC) are types of Non Discretionary Access Control (NDAC).
Tip:
When you have two answers that are synonymous they are not the right choice for sure.
There is only one access control model that makes use of Label, Clearances, and Categories, it is Mandatory Access Control, none of the other one makes use of those items.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 33).
Which of the following ports does NOT normally need to be open for a mail server to operate?
Port 110
Port 25
Port 119
Port 143
Port 119 is normally used for the Network News Transfer Protocol. It is thus not need for a mail server, which would normally listen to ports 25 (SMTP), 110 (POP3) and 143 (IMAP).
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 1: Understanding Firewalls.
What can be defined as the maximum acceptable length of time that elapses before the unavailability of the system severely affects the organization?
Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
Recovery Time Period (RTP)
Critical Recovery Time (CRT)
One of the results of a Business Impact Analysis is a determination of each business function's Recovery Time Objectives (RTO). The RTO is the amount of time allowed for the recovery of a business function. If the RTO is exceeded, then severe damage to the organization would result.
The Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) is the point in time in which data must be restored in order to resume processing.
Reference(s) used for this question:
BARNES, James C. & ROTHSTEIN, Philip J., A Guide to Business Continuity Planning, John Wiley & Sons, 2001 (page 68).
and
And: SWANSON, Marianne, & al., National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST Special Publication 800-34, Contingency Planning Guide for Information Technology Systems, December 2001 (page 47).
Which backup method usually resets the archive bit on the files after they have been backed up?
Incremental backup method.
Differential backup method.
Partial backup method.
Tape backup method.
The incremental backup method usually resets the archive bit on the files after they have been backed up.
An Incremental Backup will backup all the files that have changed since the last Full Backup (the first time it is run after a full backup was previously completed) or after an Incremental Backup (for the second backup and subsequent backups) and sets the archive bit to 0. This type of backup take less time during the backup phase but it will take more time to restore.
The other answers are all incorrect choices.
The following backup types also exists:
Full Backup - All data are backed up. The archive bit is cleared, which means that it is set to 0.
Differential Backup - Backup the files that have been modified since the last Full Backup. The archive bit does not change. Take more time while the backup phase is performed and take less time to restore.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 69.
To understand the 'whys' in crime, many times it is necessary to understand MOM. Which of the following is not a component of MOM?
Opportunities
Methods
Motivation
Means
To understand the whys in crime, many times it is necessary to understand the Motivations, Opportunities, and Means (MOM). Motivations are the who and why of a crime. Opportunities are the where and when of a crime, and Means pertains to the capabilities a criminal would need to be successful. Methods is not a component of MOM.
Which of the following is a CHARACTERISTIC of a decision support system (DSS) in regards to Threats and Risks Analysis?
DSS is aimed at solving highly structured problems.
DSS emphasizes flexibility in the decision making approach of users.
DSS supports only structured decision-making tasks.
DSS combines the use of models with non-traditional data access and retrieval functions.
DSS emphasizes flexibility in the decision-making approach of users. It is aimed at solving less structured problems, combines the use of models and analytic techniques with traditional data access and retrieval functions and supports semi-structured decision-making tasks.
DSS is sometimes referred to as the Delphi Method or Delphi Technique:
The Delphi technique is a group decision method used to ensure that each member gives an honest opinion of what he or she thinks the result of a particular threat will be. This avoids a group of individuals feeling pressured to go along with others’ thought processes and enables them to participate in an independent and anonymous way. Each member of the group provides his or her opinion of a certain threat and turns it in to the team that is performing the analysis. The results are compiled and distributed to the group members, who then write down their comments anonymously and return them to the analysis group. The comments are compiled and redistributed for more comments until a consensus is formed. This method is used to obtain an agreement on cost, loss values, and probabilities of occurrence without individuals having to agree verbally.
Here is the ISC2 book coverage of the subject:
One of the methods that uses consensus relative to valuation of information is the consensus/modified Delphi method. Participants in the valuation exercise are asked to comment anonymously on the task being discussed. This information is collected and disseminated to a participant other than the original author. This participant comments upon the observations of the original author. The information gathered is discussed in a public forum and the best course is agreed upon by the group (consensus).
EXAM TIP:
The DSS is what some of the books are referring to as the Delphi Method or Delphi Technique. Be familiar with both terms for the purpose of the exam.
The other answers are incorrect:
'DSS is aimed at solving highly structured problems' is incorrect because it is aimed at solving less structured problems.
'DSS supports only structured decision-making tasks' is also incorrect as it supports semi-structured decision-making tasks.
'DSS combines the use of models with non-traditional data access and retrieval functions' is also incorrect as it combines the use of models and analytic techniques with traditional data access and retrieval functions.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 91). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
and
Schneiter, Andrew (2013-04-15). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition : Information Security Governance and Risk Management ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 1424-1426). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following statements pertaining to a security policy is incorrect?
Its main purpose is to inform the users, administrators and managers of their obligatory requirements for protecting technology and information assets.
It specifies how hardware and software should be used throughout the organization.
It needs to have the acceptance and support of all levels of employees within the organization in order for it to be appropriate and effective.
It must be flexible to the changing environment.
A security policy would NOT define how hardware and software should be used throughout the organization. A standard or a procedure would provide such details but not a policy.
A security policy is a formal statement of the rules that people who are given access to anorganization's technology and information assets must abide. The policy communicates the security goals to all of the users, the administrators, and the managers. The goals will be largely determined by the following key tradeoffs: services offered versus security provided, ease of use versus security, and cost of security versus risk of loss.
The main purpose of a security policy is to inform the users, the administrators and the managers of their obligatory requirements for protecting technology and information assets.
The policy should specify the mechanisms through which these requirements can be met. Another purpose is to provide a baseline from which to acquire, configure and audit computer systems and networks for compliance with the policy. In order for a security policy to be appropriate and effective, it needs to have the acceptance and support of all levels of employees within the organization. A good security policy must:
• Be able to be implemented through system administration procedures, publishing of acceptable use guidelines, or other appropriate methods
• Be able to be enforced with security tools, where appropriate, and with sanctions, where actual prevention is not technically feasible
• Clearly define the areas of responsibility for the users, the administrators, and the managers
• Be communicated to all once it is established
• Be flexible to the changing environment of a computer network since it is a living document
Reference(s) used for this question:
National Security Agency, Systems and Network Attack Center (SNAC),The 60 Minute Network Security Guide, February 2002, page 7.
or
A local copy is kept at:
https://www.freepracticetests.org/documents/The%2060%20Minute%20Network%20Security%20Guide.pdf
An Architecture where there are more than two execution domains or privilege levels is called:
Ring Architecture.
Ring Layering
Network Environment.
Security Models
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are a mechanism to protect data and functionality from faults (fault tolerance) and malicious behavior (computer security). This approach is diametrically opposite to that of capability-based security.
Computer operating systems provide different levels of access to resources. A protection ring is one of two or more hierarchical levels or layers of privilege within the architecture of a computer system. This is generally hardware-enforced by some CPU architectures that provide different CPU modes at the hardware or microcode level. Rings are arranged in a hierarchy from most privileged (most trusted, usually numbered zero) to least privileged (least trusted, usually with the highest ring number). On most operating systems, Ring 0 is the level with the most privileges and interacts most directly with the physical hardware such as the CPU and memory.
Special gates between rings are provided to allow an outer ring to access an inner ring's resources in a predefined manner, as opposed to allowing arbitrary usage. Correctly gating access between rings can improve security by preventing programs from one ring or privilege level from misusing resources intended for programs in another. For example, spyware running as a user program in Ring 3 should be prevented from turning on a web camera without informing the user, since hardware access should be a Ring 1 function reserved for device drivers. Programs such as web browsers running in higher numbered rings must request access to the network, a resource restricted to a lower numbered ring.
Ring Architecture
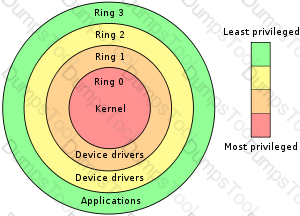
All of the other answers are incorrect because they are detractors.
References:
OIG CBK Security Architecture and Models (page 311)
and
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_%28computer_security%29
What can be defined as: It confirms that users’ needs have been met by the supplied solution ?
Accreditation
Certification
Assurance
Acceptance
Acceptance confirms that users’ needs have been met by the supplied solution. Verification and Validation informs Acceptance by establishing the evidence – set against acceptance criteria - to determine if the solution meets the users’ needs. Acceptance should also explicitly address any integration or interoperability requirements involving other equipment or systems. To enable acceptance every user and system requirement must have a 'testable' characteristic.
Accreditation is the formal acceptance of security, adequacy, authorization for operation and acceptance of existing risk. Accreditation is the formal declaration by a Designated Approving Authority (DAA) that an IS is approved to operate in a particular security mode using a prescribed set of safeguards to an acceptable level of risk.
Certification is the formal testing of security safeguards and assurance is the degree of confidence that the implemented security measures work as intended. The certification is a Comprehensive evaluation of the technical and nontechnical security features of an IS and other safeguards, made in support of the accreditation process, to establish the extent to which a particular design and implementation meets a set of specified ecurity requirements.
Assurance is the descriptions of the measures taken during development and evaluation of the product to assure compliance with the claimed security functionality. For example, an evaluation may require that all source code is kept in a change management system, or that full functional testing is performed. The Common Criteria provides a catalogue of these, and the requirements may vary from one evaluation to the next. The requirements for particular targets or types of products are documented in the Security Targets (ST) and Protection Profiles (PP), respectively.
Source: ROTHKE, Ben, CISSP CBK Review presentation on domain 4, August 1999.
and
Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Second Edition, on page 211.
and
http://www.aof.mod.uk/aofcontent/tactical/randa/content/randaintroduction.htm
What is the goal of the Maintenance phase in a common development process of a security policy?
to review the document on the specified review date
publication within the organization
to write a proposal to management that states the objectives of the policy
to present the document to an approving body
"publication within the organization" is the goal of the Publication Phase "write a proposal to management that states the objectives of the policy" is part of Initial and Evaluation Phase "Present the document to an approving body" is part of Approval Phase.
Buffer overflow and boundary condition errors are subsets of which of the following?
Race condition errors.
Access validation errors.
Exceptional condition handling errors.
Input validation errors.
In an input validation error, the input received by a system is not properly checked, resulting in a vulnerability that can be exploited by sending a certain input sequence. There are two important types of input validation errors: buffer overflows (input received is longer than expected input length) and boundary condition error (where an input received causes the system to exceed an assumed boundary). A race condition occurs when there is a delay between the time when a system checks to see if an operation is allowed by the security model and the time when the system actually performs the operation. In an access validation error, the system is vulnerable because the access control mechanism is faulty. In an exceptional condition handling error, the system somehow becomes vulnerable due to an exceptional condition that has arisen.
Source: DUPUIS, Clement, Access Control Systems and Methodology CISSP Open Study Guide, version 1.0, march 2002 (page 105).
Which of the following was designed to support multiple network types over the same serial link?
Ethernet
SLIP
PPP
PPTP
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) was designed to support multiple network types over the same serial link, just as Ethernet supports multiple network types over the same LAN. PPP replaces the earlier Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) that only supports IP over a serial link. PPTP is a tunneling protocol.
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 3: TCP/IP from a Security Viewpoint.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) interrogates the network by sending out a?
broadcast.
multicast.
unicast.
semicast.
ARP interrogates the network by sending out a broadcast seeking a network node that has a specific IP address, and asks it to reply with its hardware address. A broadcast message is sent to everyone whether or not the message was requested. A traditional unicast is a "one-to-one" or "narrowcast" message. A multicast is a "one-to-many" message that is traditionally only sent to those machine that requested the information. Semicast is an imposter answer.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 87.
Which of the following category of UTP cables is specified to be able to handle gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) according to the EIA/TIA-568-B standards?
Category 5e UTP
Category 2 UTP
Category 3 UTP
Category 1e UTP
Categories 1 through 6 are based on the EIA/TIA-568-B standards.
On the newer wiring for LANs is CAT5e, an improved version of CAT5 which used to be outside of the standard, for more information on twisted pair, please see: twisted pair.
Category Cable Type Mhz Usage Speed
=============================================
CAT1 UTP Analog voice, Plain Old Telephone System (POTS)
CAT2 UTP 4 Mbps on Token Ring, also used on Arcnet networks
CAT3 UTP, ScTP, STP 16 MHz 10 Mbps
CAT4 UTP, ScTP, STP 20 MHz 16 Mbps on Token Ring Networks
CAT5 UTP, ScTP, STP 100 MHz 100 Mbps on ethernet, 155 Mbps on ATM
CAT5e UTP, ScTP, STP 100 MHz 1 Gbps (out of standard version, improved version of CAT5)
CAT6 UTP, ScTP, STP 250 MHz 10 Gbps
CAT7 ScTP, STP 600 M 100 Gbps
Category 6 has a minumum of 250 MHz of bandwidth. Allowing 10/100/1000 use with up to 100 meter cable length, along with 10GbE over shorter distances.
Category 6a or Augmented Category 6 has a minimum of 500 MHz of bandwidth. It is the newest standard and allows up to 10GbE with a length up to 100m.
Category 7 is a future cabling standard that should allow for up to 100GbE over 100 meters of cable. Expected availability is in 2013. It has not been approved as a cable standard, and anyone now selling you Cat. 7 cable is fooling you.
REFERENCES:
http://donutey.com/ethernet.php
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TIA/EIA-568-B
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category_1_cable
Java is not:
Object-oriented.
Distributed.
Architecture Specific.
Multithreaded.
JAVA was developed so that the same program could be executed on multiple hardware and operating system platforms, it is not Architecture Specific.
The following answers are incorrect:
Object-oriented. Is not correct because JAVA is object-oriented. It should use the object-oriented programming methodology.
Distributed. Is incorrect because JAVA was developed to be able to be distrubuted, run on multiple computer systems over a network.
Multithreaded. Is incorrect because JAVA is multi-threaded that is calls to subroutines as is the case with object-oriented programming.
A virus is a program that can replicate itself on a system but not necessarily spread itself by network connections.
In computing what is the name of a non-self-replicating type of malware program containing malicious code that appears to have some useful purpose but also contains code that has a malicious or harmful purpose imbedded in it, when executed, carries out actions that are unknown to the person installing it, typically causing loss or theft of data, and possible system harm.
virus
worm
Trojan horse.
trapdoor
A trojan horse is any code that appears to have some useful purpose but also contains code that has a malicious or harmful purpose imbedded in it. A Trojan often also includes a trapdoor as a means to gain access to a computer system bypassing security controls.
Wikipedia defines it as:
A Trojan horse, or Trojan, in computing is a non-self-replicating type of malware program containing malicious code that, when executed, carries out actions determined by the nature of the Trojan, typically causing loss or theft of data, and possible system harm. The term is derived from the story of the wooden horse used to trick defenders of Troy into taking concealed warriors into their city in ancient Greece, because computer Trojans often employ a form of social engineering, presenting themselves as routine, useful, or interesting in order to persuade victims to install them on their computers.
The following answers are incorrect:
virus. Is incorrect because a Virus is a malicious program and is does not appear to be harmless, it's sole purpose is malicious intent often doing damage to a system. A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates by inserting copies of itself (possibly modified) into other computer programs, data files, or the boot sector of the hard drive; when this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected".
worm. Is incorrect because a Worm is similiar to a Virus but does not require user intervention to execute. Rather than doing damage to the system, worms tend to self-propagate and devour the resources of a system. A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer.
trapdoor. Is incorrect because a trapdoor is a means to bypass security by hiding an entry point into a system. Trojan Horses often have a trapdoor imbedded in them.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trojan_horse_%28computing%29
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_virus
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_worm
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backdoor_%28computing%29

TESTED 23 Feb 2026
Copyright © 2014-2026 DumpsTool. All Rights Reserved
