You are deploying a site-to-site IPsec VPN connection between your on-premise subnet and your Azure VNets.
What is the most important advantage for using FortiGate at both ends of the tunnel?
Refer to the exhibit.
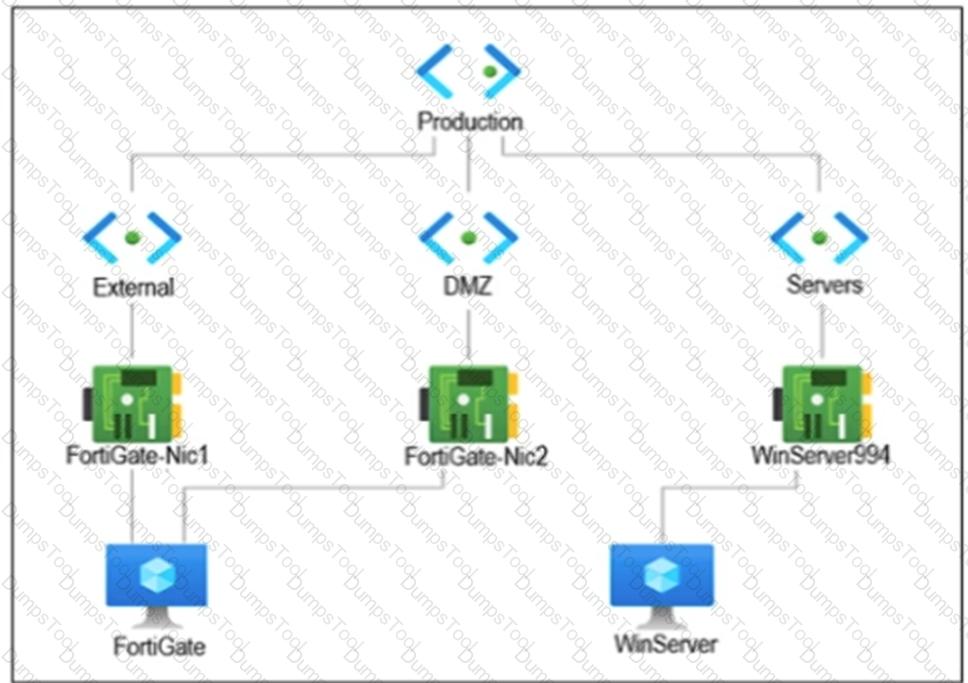
You are troubleshooting a network connectivity issue between two VMs that are deployed in Azure.
One VM is a FortiGate that has one interface in the DMZ subnet, which is in the Production VNet. The other VM is a Windows Server in the Servers subnet, which is also in the Production VNet. You cannot ping the Windows Server from the FortiGate VM.
What is the reason for this?
How are the configurations synchronized between two FortiGate VMs in an active-passive HA with SDN connector failover deployed from the Azure marketplace?
A Linux server was deployed in a protected subnet with a dynamic IP address. A FortiGate VM in the internal subnet provides traffic filtering to it. and you must implement a firewall policy using the IP address of the Linux server.
Which feature could help integrate FortiGate using Linux server tags?